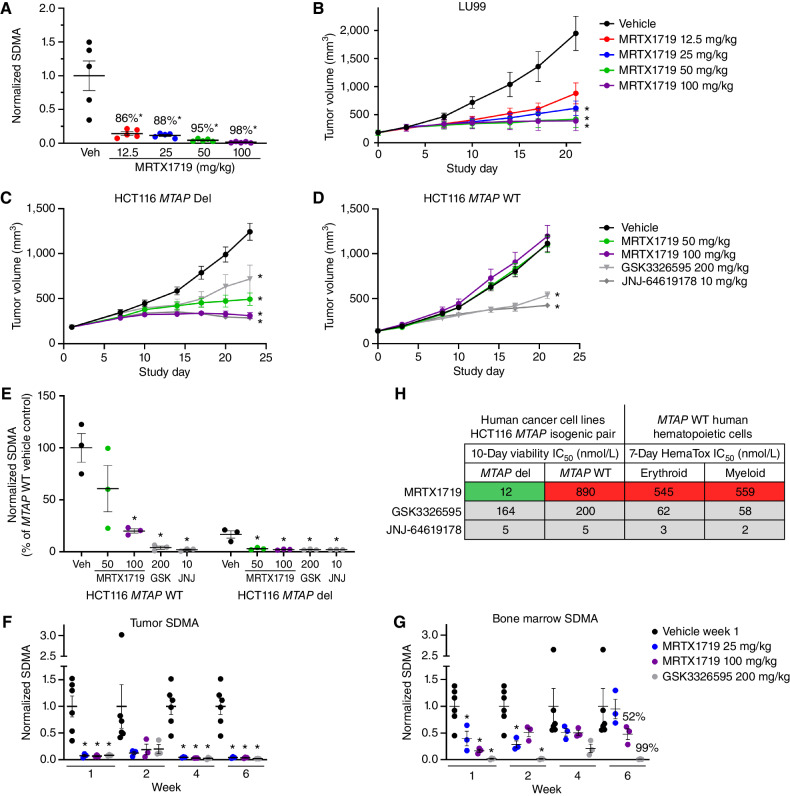
Figure 2.
MRTX1719 exhibits selective, dose-dependent inhibition of PRMT5-dependent SDMA modification in MTAP del tumor xenografts in vivo. A, MRTX1719 was administered daily via daily oral gavage for 22 days to immunocompromised mice bearing LU99 tumor xenografts (average initial tumor volume ∼180 mm3) at 12.5, 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg. Tumors were collected 4 hours after dose, and SDMA was analyzed by immunoblot and quantified with densitometry. Average normalized SDMA values were divided by the average value in vehicle-treated tumors to calculate percent inhibition. Data shown represent the average of 2 to 3 tumors per treatment group ± SEM. Statistics were determined using a two-tailed Student t test with significance indicated (*, P < 0.05). Veh, vehicle. B, MRTX1719 was administered at the indicated doses via daily oral gavage to mice bearing established LU99 cell line–derived tumor xenografts as in A. Data, mean tumor volume ± SEM. Statistics were determined using a two-way ANOVA with significance indicated (*, P < 0.05). A and B were previously published in Smith et al. (14). C and D, MRTX1719, GSK3326595, or JNJ-64619178 was administered via daily oral gavage at the doses indicated to mice bearing established HCT116 MTAP del (C) or MTAP WT (D) cell line–derived tumor xenografts. Dosing was initiated when tumors were ∼150 mm3. Data, mean tumor volume ± SEM. Statistics were determined using a two-way ANOVA with significance indicated (*, P < 0.05). E, Tumors from the HCT116 MTAP WT or HCT116 MTAP del cell line–derived xenografts in C and D were collected 4 hours after dose, and SDMA was analyzed by immunoblot. Data shown represent the average of 3 tumors per treatment group ± SEM. Statistics were determined using a two-tailed Student t test with significance indicated (*, P < 0.05). GSK, GSK3326595; JNJ, JNJ-64619178. F and G, MRTX1719 and GSK3326595 were administered via daily oral gavage to immunocompromised mice bearing established LU99 xenograft tumors at the indicated doses for the indicated number of weeks. Tumor (F) and bone marrow (G) were collected 4 hours after last dose, and SDMA was analyzed by Western blot densitometry. Representative SDMA bands were analyzed from 3 to 5 tumor lysates and bone marrow lysates from 3 to 5 mice per treatment group, and data are shown as mean normalized SDMA levels ± SEM. Statistics were determined using a two-tailed Student t test with significance indicated (*, P < 0.05). H, MRTX1719, JNJ-64619178, and GSK3326595 were run in human erythroid and myeloid 7-day HemaTox assays (STEMCELL Technologies) and were compared with IC50 values from 10-day HCT116 MTAP del and MTAP WT cell line viability assays.