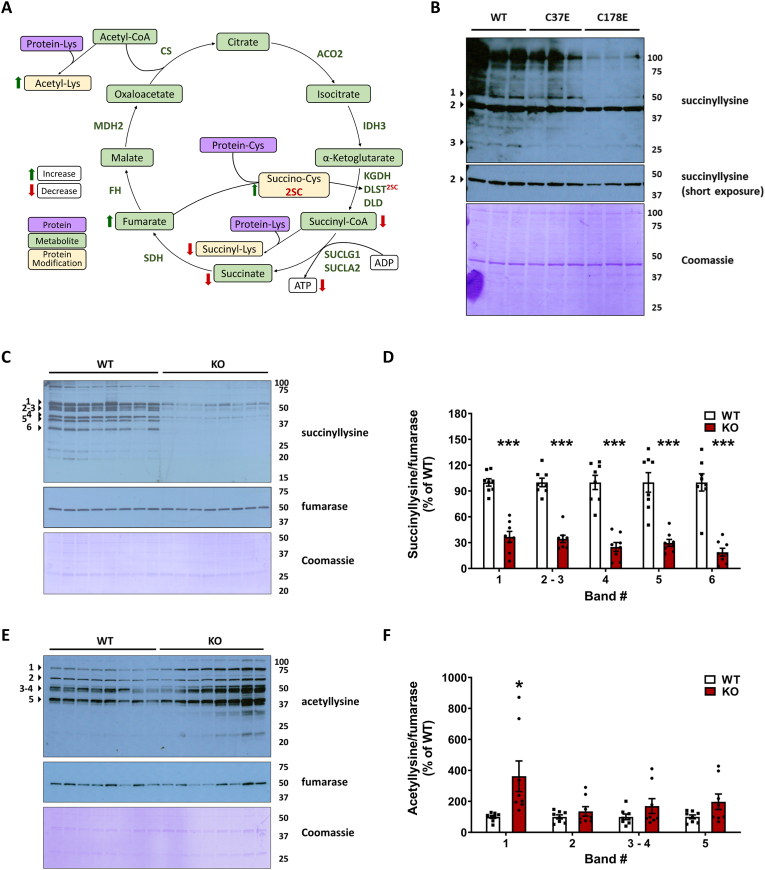
Fig. 6.
DLST succination and mutations that mimic DLST succination alter the levels of protein acylation in vivo and in vitro.A, Schematic illustrating TCA cycle deficits in the Ndufs4 KO mouse. Red arrows indicate a measured decrease and green arrows indicate a measured increase. The metabolic impact of a 2-fold increase in fumarate (P < 0.001) contributes to a 2-fold increase in protein succination (P < 0.05). The specific succination of DLST (DLST2SC) contributes to a 25–30 % decrease in KGDHC activity (P < 0.001), and results in lower ATP via a 48 % reduction in SUCLA activity (P < 0.05), decreased lysine succinylation (hyposuccinylation), and a 50 % reduction in succinate levels (P < 0.001). Lysine acetylation of select proteins increases as a consequence of diminished TCA cycle function. These metabolic perturbations impacting the TCA cycle alter the chemical modification of proteins, extending the biochemical deficit beyond the loss of the Complex I component Ndufs4. Relationships between metabolites (green boxes), protein lysine or cysteine residues (purple boxes) and protein modifications (yellow boxes) are indicated. B, Protein lysine succinylation in mitochondrial fractions obtained from DLST KO H838 cells expressing WT hDLST, C37E or C178E hDLST succinomimetic mutants. C, Protein lysine succinylation in mitochondrial fractions obtained from the brainstem of WT and Ndufs4 KO mice. D, Quantification of prominent bands in C (indicated by arrowheads). E, Protein lysine acetylation in mitochondrial fractions obtained from brainstem of WT and Ndufs4 KO mice. F, Quantification of prominent bands in E (indicated by arrowheads).In B, Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining (prominent band at 42 kDa) was used for the normalization of the succinyllysine signal. In C and E, re-probing to detect fumarase was used for mitochondrial protein normalization, followed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. Molecular weight markers are shown on the right side. See also Fig. S4. In D and F, results expressed as mean ± SEM were compared by unpaired t-test (*p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 vs. WT). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)