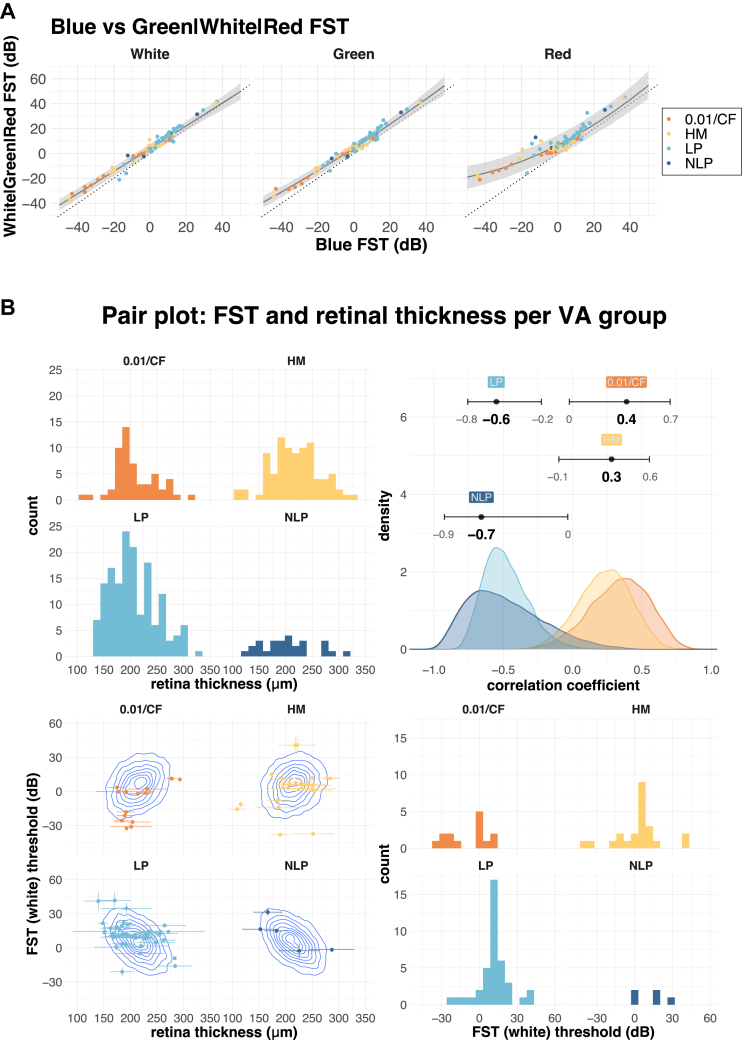
Figure 8.
A, Relationship between full-field stimulus testing (FST) values for blue, white, green and red light. The blue FST value was plotted against white, green, and red FST values. The dotted diagonal line has an intercept of 0 and a slope of 1. Points above the dotted line indicate a higher FST value than blue light, and points below the dotted line indicate a lower FST value. The solid line shows the mean, and the shaded area shows the 95% compatibility interval of quadratic regression for each of the colors. B, Relationship between retinal thickness and FST (white) stratified by 4 visual acuity (VA) groups. The upper left panel shows the distribution of retinal thickness, and the lower right panel shows the distribution of FST for white light. The lower left panel shows the distribution of the data (points) overlayed with estimated correlation (density plot), with horizontal error bars showing the standard deviation of retinal thickness measurement (average of 4 points), and vertical error bars showing the estimated error (standard deviation) from the FST analysis. The upper right panel shows the distribution of posterior estimates for the correlation between FST and retinal thickness (error bars show 95% confidence interval). CF = counting fingers; dB = decibels; HM = hand motion; LP = light perception; NLP = no light perception.