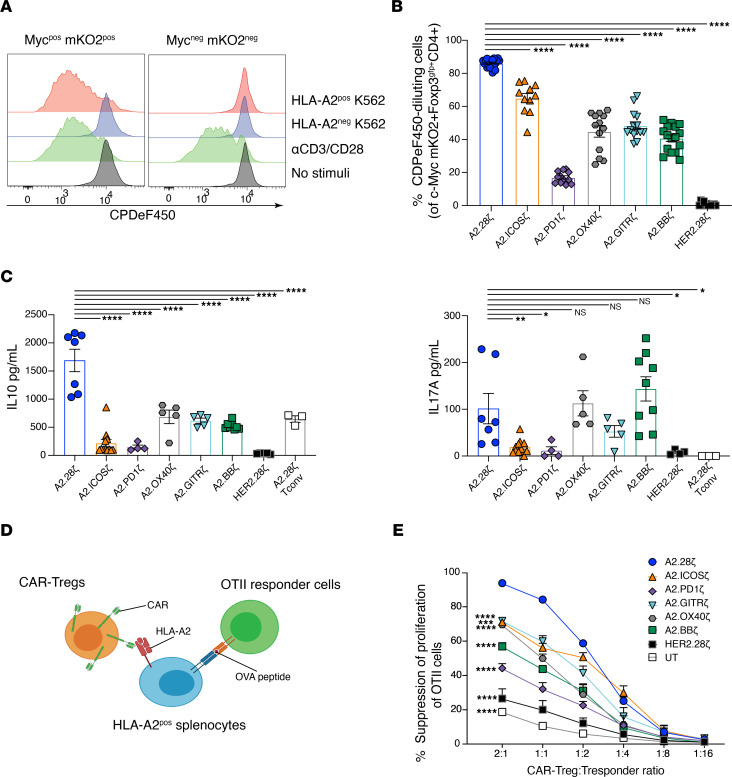
Figure 2. Costimulatory CAR variants differ in their ability to stimulate Tregs.
(A–C) Tregs expressing the indicated CAR were stained with CPDe450 and cocultured with HLA-A2+ or HLA-A2– K562 cells, polyclonal stimulated with anti-CD3/28, or left unstimulated for 3 days. (A) Representative histograms of at least 5 independent experiments comparing A2.28ζ CAR-Treg proliferation of gated CAR+ (c-Myc+mKO2+) or CAR– (c-Myc–mKO2–) cells. (B) Frequencies of CAR-Tregs that divided after 3 days of coculture with HLA-A2+ K562s, determined by CPDeF450 dilution, gated on c-Myc+mKO2+Foxp3gfp+CD4+ cells; n = 11–20 replicates from at least 5 independent experiments. (C) Cytokine secretion after 3 days of coculture with HLA-A2+ K562s; n = 3–12 replicates from at least 3 independent experiments. (D and E) CAR-Tregs were cocultured with OTII CD4+ T cells at varying ratios in the presence of irradiated HLA-A2+ splenocytes and OVA peptide. (D) Schematic diagram of the linked suppression assay. (E) CAR-Treg–mediated suppression of the OTII CD4+ T cell proliferation, as determined by Ki67 expression; n = 3–6 replicates from at least 2 independent experiments. Tresponder, responder T cell; UT, untransduced. Data are reported as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using 1-way (B and C) or 2-way (E) ANOVA with a Holm-Šidak posttest comparing to CD28-based CAR-Tregs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.