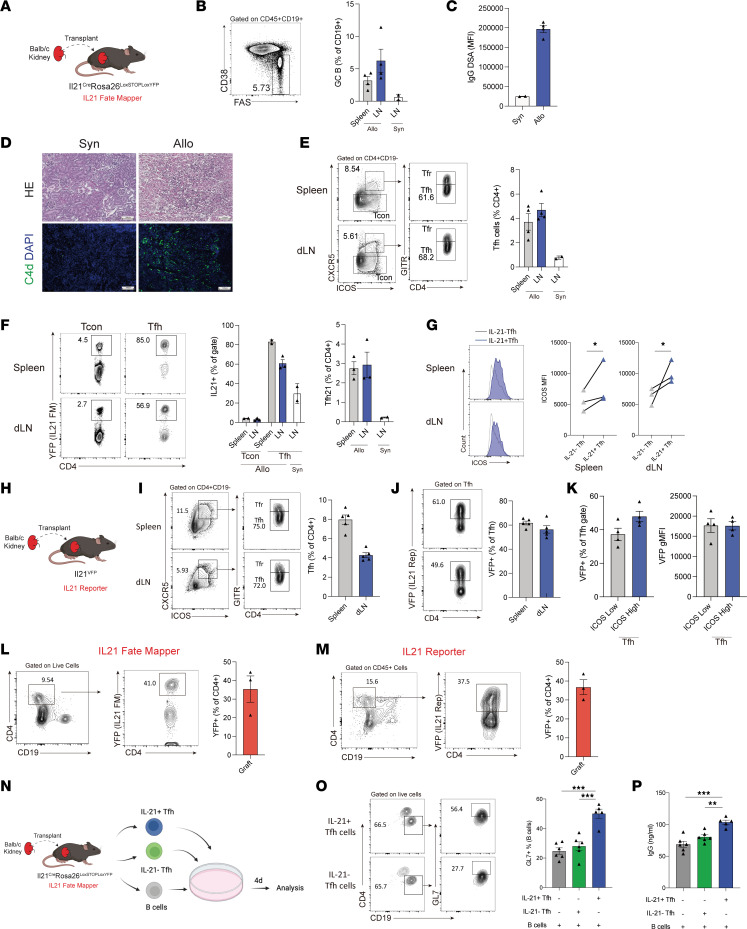
Figure 1. IL-21–producing Tfh cells are generated in LNs and grafts after allogeneic kidney transplantation.
(A) Schematic of kidney transplantation. (B) Gating strategy (left) and quantification of FAS+CD38– GC B cells (right) in the spleen and dLN. (C) DSA IgG measurements from serum. (D) Histology and C4d IF in grafts. Scale bars: 100 μm; original magnification: ×100. (E) Quantification of Tfh (CD4+CD19–CXCR5+ICOS+GITR–) cells in the spleen and dLN. Representative gating (left) and quantification (right) are shown. (F) Gating strategy (left) and quantification (right) of IL-21 fate mapped (YFP+) Tcon and Tfh cells. Gated on CD4+CD19–CXCR5+ICOS+ cells. (G) Expression of ICOS in IL-21 fate-mapped (IL-21+) or nonfate-mapped (IL-21–) Tfh cells. (H) Schematic of kidney transplantation of Balb/c kidneys into IL-21 direct reporter mice. (I) Gating strategy (left) and quantification (right) of total Tfh cells. (J) Gating strategy (left) and quantification (right) of IL-21–expressing (VFP+) Tfh cells. (K) Frequency (left) and MFI (right) of VFP+ cells in ICOS low and high Tfh cells. gMFI, geometric MFI. (L and M) Quantification of IL-21–producing (YFP+, and VFP+) graft-infiltrating CD4+ T cells. In A–M, data are combined from 2 independent experiments, n = 2–5 mice replicates per group. (N) Schematic of in vitro Tfh-mediated B cell stimulation assay. IL-21 fate-mapped (IL-21+), nonfate-mapped (IL-21–) Tfh, and B cells from recipients were cocultured for 4 days with anti-CD3/IgM. (O) Gating strategy (left) and quantification (right) of activated (GL7+) B cells. (P) IgG concentration in culture supernatants of the in vitro assays. In O and P, data are from 1 experiment and are representative of 2 independent experiments, n = 5–6 wells per group. Student’s 2-tailed unpaired t test for G, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test for O and P. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.