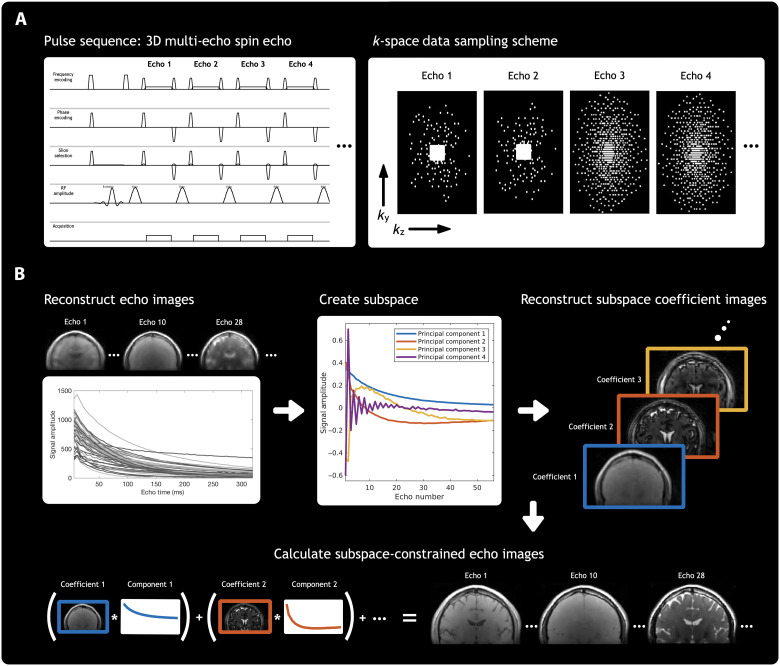
Fig. 7. CALIPR framework acquisition and reconstruction.
A graphical overview of the CALIPR framework methodology. For (A) acquisition and (B) reconstruction. For (A) image acquisition, the pulse sequence phase encoding gradients are modified to sample data incoherently across the additional nonspatial dimension present for many magnetic resonance imaging techniques. For (B) reconstruction, images from an initial naïve reconstruction are used to generate a subspace, calibrated for that specific dataset. A second and final reconstruction is then performed, explicitly constrained to this low-dimensional subspace. This combined acquisition and reconstruction framework exploits redundancy present in additional, nonspatial dimensions of the data by sampling in a way that makes under sampling artifacts less coherent and therefore more easily suppressed by a sparsity-promoting reconstruction, while true image features remain coherent and easily recoverable.