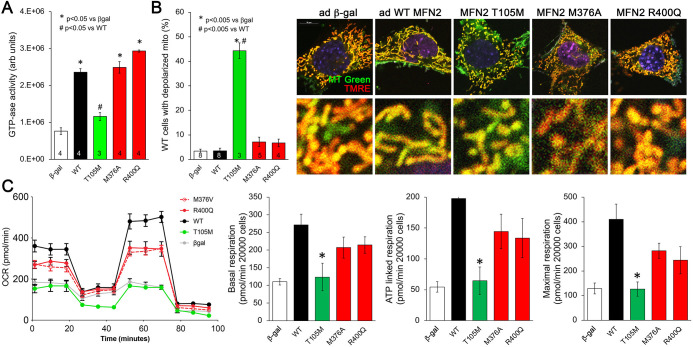
Figure 2. Effects of disease-related MFN2 mutants on catalytic and respiratory function of mitofusin null and normal mitochondria.
(A) GTPase activity of human disease-linked MFN2 mutants expressed in mitofusin double knockout (DKO) murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). (B) Loss of inner membrane polarization in WT MEF mitochondria induced by disease-related MFN2 mutants. To the right are representative MitoTracker Green/TMRE co-stained confocal images. (C) Seahorse studies of oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in MFN DKO MEFs expressing disease-linked MFN2 mutants. (Left) Average data from three experiments per condition. (Right) Group quantitative results for basal, ATP-linked and maximal respiration (pmol/min/20,000 cells). *p<0.05 vs. WT.p-Values for all studies used ANOVA and Tukey’s test.
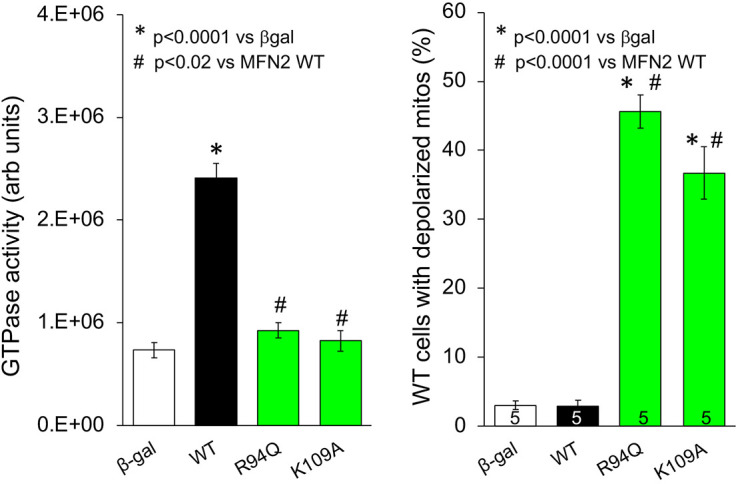
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. GTPase activity of, and inner membrane depolarization induced by, GTPase domain CMT2A-linked MFN2 R94Q and laboratory-engineered K109A expressed in Mfn1/Mfn2 double knockout (DKO) murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) (left) and WT MEFs (right), respectively.