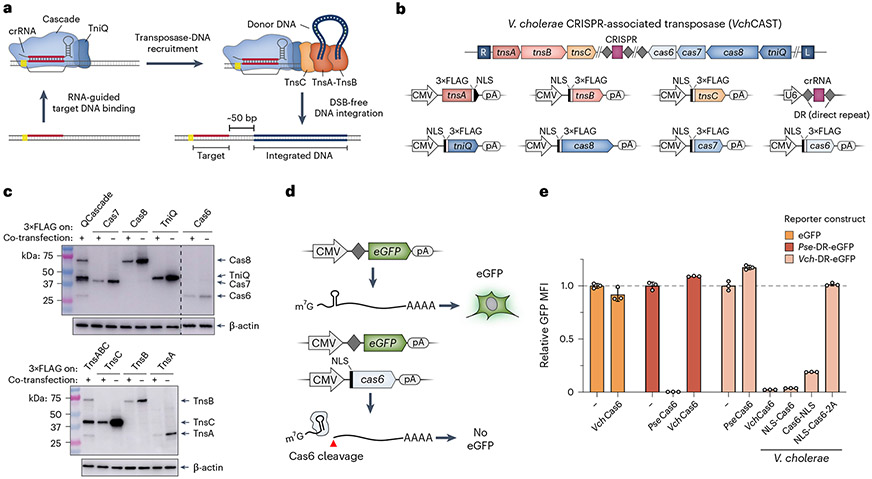
Fig. 1 ∣. Reconstitution of protein–RNA CAST components in human cells.
a, Schematic detailing DNA integration using RNA-guided transposases. b, Type I-F CRISPR-associated transposons encode the CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and seven proteins needed for DNA integration (top). Mammalian expression vectors used for heterologous reconstitution in human cells are shown at the bottom. c, Western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody demonstrates robust protein expression upon individual (−) or multi-plasmid (+) co-transfection of HEK293T cells. Co-transfections contained all VchCAST components, with the FLAG-tagged subunit(s) indicated. β-actin was used as a loading control. Western blots were repeated in biological duplicates with similar results. d, Schematic of eGFP knockdown assay to monitor crRNA processing by Cas6 in HEK293T cells. Cleavage of the CRISPR direct repeat (DR)-encoded stem-loop severs the 5′ cap from the ORF and polyA (pA) tail, leading to a loss of eGFP fluorescence (bottom). e, Transposon-encoded VchCas6 (Type I-F3) exhibits efficient RNA cleavage and eGFP knockdown, as measured by flow cytometry. Knockdown was similar to PseCas6 from a canonical CRISPR–Cas system (Type I-E)41, was absent with a non-cognate DR substrate and was sensitive to C-terminal tagging. To control for overexpression, data were normalized to negative control conditions (−), in which dCas9 was co-transfected with the reporter. Data are shown as the mean ± s.d. for n = 3 biologically independent samples. Uncropped western blots are shown in Source Data Fig. 1.