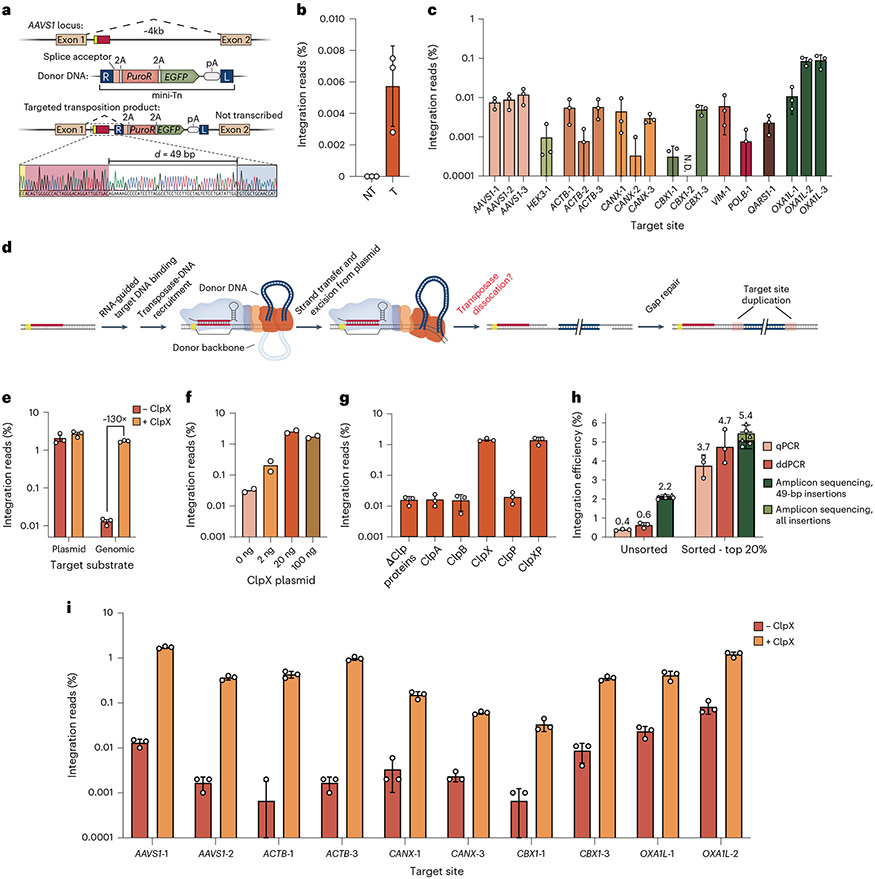
Fig. 5 ∣. ClpX-mediated enhancement of genomic DNA integration with eCAST-3.
a, Sanger sequencing of nested PCR of genomic lysates In which eCAST-2.2 targeted the AAVS1 genome and showed a junction product 49 bp downstream of the target site targeted by crRNA12 (AAVS1-1), one of the optimal crRNAs screened in Supplementary Fig. 10a. b, Initial quantifications of genomic integration efficiencies at AAVS1-1. c, Integration efficiencies across multiple loci within human genome showed broadly limited efficiencies. Quantified integration efficiencies less than 0.0001% were not plotted, and ‘N.D.’ represents a target site in which no integration events were detected across three biological replicates. d, Proposed steps required for successful targeted integration, including the downstream gap repair needed for complete resolution of the integration product. e, Co-transfection of EcoClpX specifically improves genomic, but not plasmid, integration efficiencies in human cells. f, Co-transfecting EcoClpX at varied amounts directly impacts genomic integration efficiencies in human cells. g, Investigating the impact of various Clp proteins from E. coli on genomic integration efficiencies in human cells. h, Integration efficiencies for samples before and after FACS of a fluorescent transfection marker to select for the top 20% brightest cells. Sorting enriched integration efficiencies, as measured by qPCR, ddPCR and amplicon sequencing (Supplementary Fig. 9b). For amplicon sequencing samples, triangle data points represent all insertions characterized, whereas circle data points represent only 49-bp insertions. i, Integration efficiencies were investigated across multiple loci within the human genome with and without EcoClpX. Quantified integration efficiencies less than 0.0001% were not plotted. Data in b, c, e and g–i are shown as the mean ± s.d. for n = 3 biologically independent samples. Data in f are shown as the mean for n = 2 biologically independent samples. Data in b, c, e, f, g and i are quantified by amplicon sequencing. FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting.