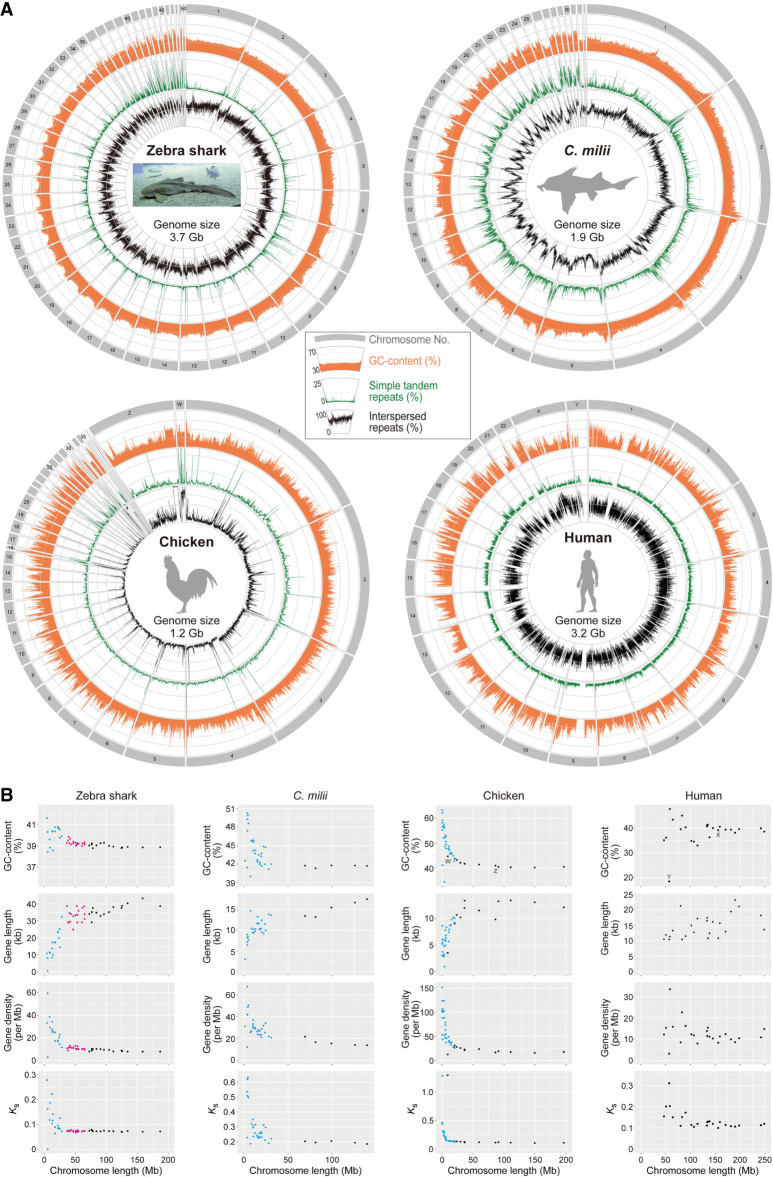
Figure 2.
Chromosomal sequence compositions of the zebra shark and selected vertebrate species. (A) Sequence characterization of different chromosomal segments. The orange areas show GC content (30%–70%), whereas the green and black lines show content of simple tandem repeats (0%–25%) and interspersed repeats (0%–100%), respectively, in 100-kb-long nonoverlapping windows. (B) Two-dimensional plots of GC content and median values of gene length, gene density, and the median of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site (Ks) for protein-coding genes on individual chromosomes. See Methods for statistical tests for correlation of these features with chromosome length. Computation of Ks was performed for each of the four species in order by involving a pair species, namely, whale shark Rhincodon typus; small-eyed rabbitfish Hydrolagus affinis; helmeted guineafowl Numida meleagris; and common marmoset Callithrix jacchus. Zebra shark chromosomes are shown as three groups, eMAC, eMID, and eMIC (see text for details), in black, magenta, and cyan, respectively, whereas microchromosomes of the chicken and Callorhinchus milii are colored in cyan. At the moment, C. milii is the only holocephalan species with a chromosome-scale genome assembly.