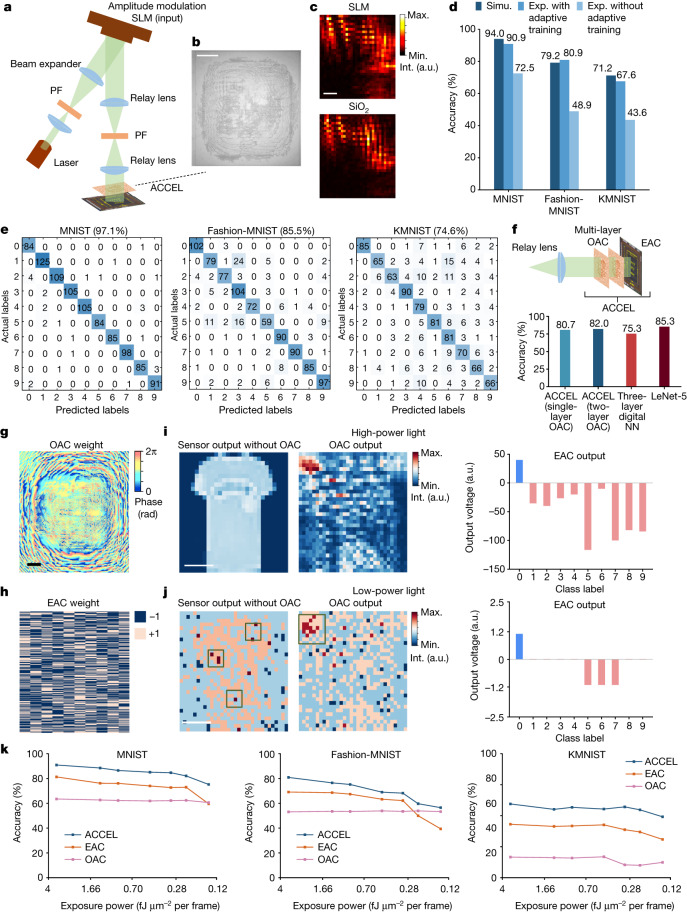
Fig. 4. Experimental results of ACCEL for image classification.
a, Experimental set-up to test ACCEL. PF, linear polarizer. The pixel size of the phase mask in OAC is 9.2 µm. b, Photograph of an etched eight-level phase mask with SiO2, serving as OAC. Scale bar, 500 μm. c, Experimental OAC output images obtained by a fixed SiO2 phase mask or a phase pattern generated by a phase-modulation SLM. Scale bar, 200 μm. d, Experimental classification accuracies of ACCEL with and without adaptive training on the MNIST, Fashion-MNIST and KMNIST datasets, compared with simulation accuracies. To match the parameters in experiments, we set the pixel size of the phase mask in OAC as 9.2 µm and the diffraction distance as 150 mm in the simulation. Simu., simulation; Exp., experiment. e, Confusion matrixes of ACCEL with single-layer small-scale digital NN (16 × 10 neurons) tested on the MNIST, Fashion-MNIST and KMNIST datasets. ACCEL and digital NN are connected through a 10-bit ADC and rectified linear unit nonlinearity is used between EAC and the digital NN. f, Experimental classification results of ACCEL with single-layer OAC and two-layer OAC on 3-class ImageNet classification, compared with digital fully connected and convolutional (LeNet-5) NNs (Supplementary Table 1). g,h, Experimental OAC weights (phase map) and EAC weights for the classification of Fashion-MNIST. Scale bar, 300 μm. i,j, Experimental example results for the Fashion-MNIST dataset with high-power light (5 fJ μm−2 per frame) (i) and low-power light (0.14 fJ μm−2 per frame) (j), including the direct output of the photodiode array with and without OAC and the output after both OAC and EAC. Scale bar, 300 μm. k, Experimental classification accuracies of ACCEL, OAC-only and EAC-only under different low-light conditions on the MNIST, Fashion-MNIST and KMNIST datasets. a.u., arbitrary unit; Max., maximum; Min., minimum; Int., intensity; Simu., simulation; Exp., experiment.