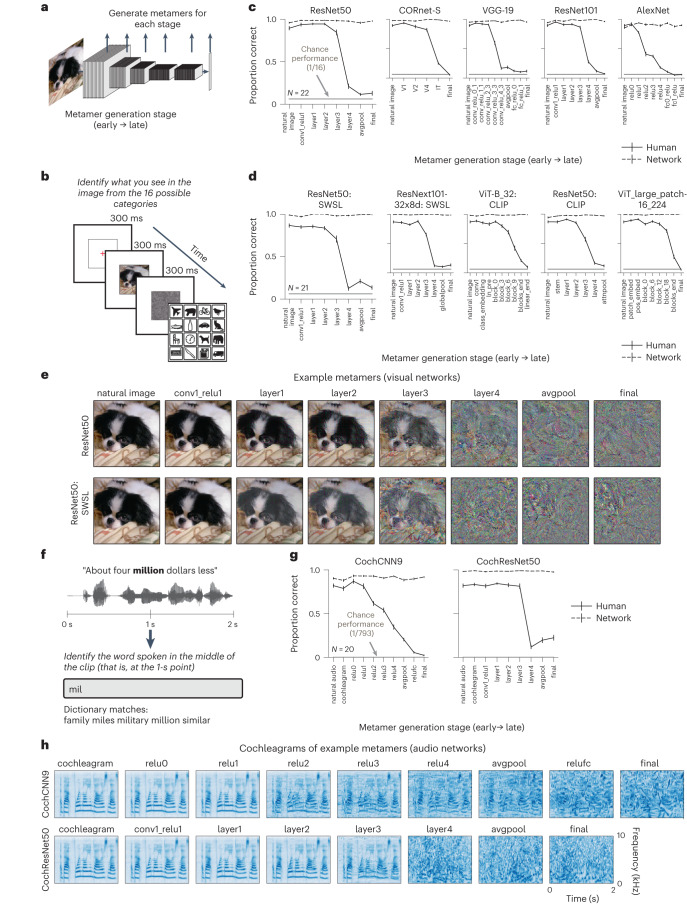
Fig. 2. Metamers of standard-trained visual and auditory deep neural networks are often unrecognizable to human observers.
a, Model metamers are generated from different stages of the model. Here and elsewhere, in models with residual connections, we only generated metamers from stages where all branches converge, which ensured that all subsequent model stages, and the model decision, remained matched. b, Experimental task used to assess human recognition of visual model metamers. Humans were presented with an image (a natural image or a model metamer of a natural image) followed by a noise mask. They were then presented with 16 icons representing 16 object categories and classified each image as belonging to one of the categories by clicking on the icon. c, Human recognition of visual model metamers (N = 22). At the time of the experiments the five models tested here placed 11th, 1st, 2nd, 4th and 59th (left to right) on a neural prediction benchmark26,31. For all tested models, human recognition of model metamers declined for late model stages, while model recognition remained high (as expected). Error bars plot s.e.m. across participants (or participant-matched stimulus subsets for model curves). d, Human recognition of visual model metamers (N = 21) trained on larger datasets. Error bars plot s.e.m. across participants (or participant-matched stimulus subsets for model curves). e, Example metamers from standard-trained and semi-weakly-supervised-learning (SWSL)-trained ResNet50 visual models. f, Experimental task used to assess human recognition of auditory model metamers. Humans classified the word that was present at the midpoint of a 2-s sound clip. Participants selected from 793 possible words by typing any part of the word into a response box and seeing matching dictionary entries from which to complete their response. A response could only be submitted if it matched an entry in the dictionary. g, Human recognition of auditory model metamers (N = 20). For both tested models, human recognition of model metamers decreased at late model stages, while model recognition remained high, as expected. When plotted, chance performance (1/793) is indistinguishable from the x axis. Error bars plot s.e.m. across participants (or participant-matched stimulus subsets for model curves). h, Cochleagram visualizations of example auditory model metamers from CochCNN9 and CochResNet50 architectures. Color intensity denotes instantaneous sound amplitude in a frequency channel (arbitrary units).