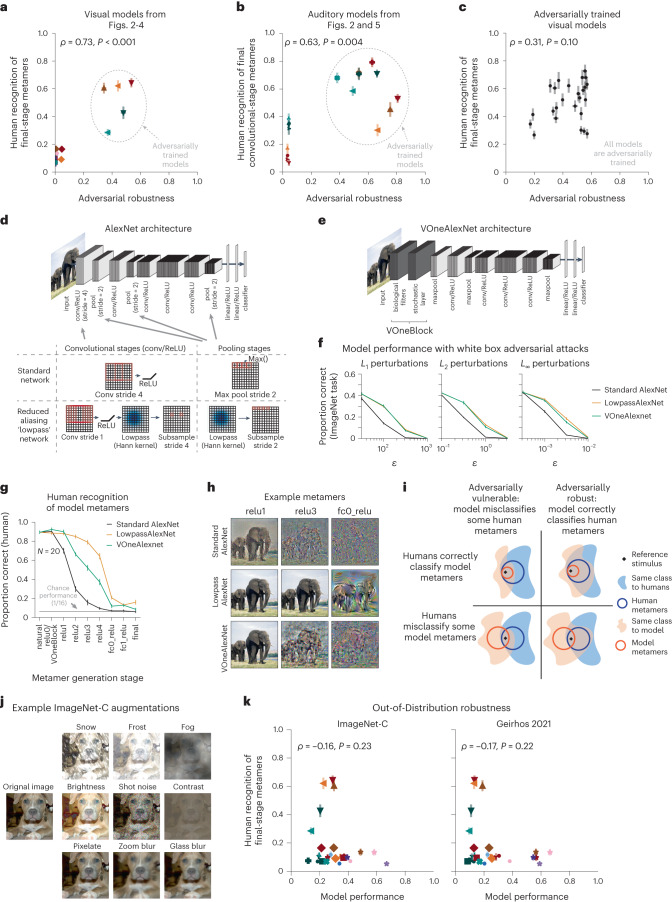
Fig. 6. Human recognition of model metamers dissociates from adversarial robustness.
a, Adversarial robustness of visual models versus human recognizability of final-stage model metamers (N = 26 models). Robustness was quantified as average robustness to L2 (ε = 3) and L∞ (ε = 4/255) adversarial examples, normalized by performance on natural images. Symbols follow those in Fig. 7a. Here and in b and c, error bars for abscissa represent s.e.m. across 5 random samples of 1,024 test examples, and error bars for ordinate represent s.e.m. across participants. b, Same as a but for final convolutional stage (CochCNN9) or block (CochResNet50) of auditory models (N = 17 models). Robustness was quantified as average robustness to L2 (ε = 10−0.5) and L∞ (ε = 10−2.5) adversarial perturbations of the waveform, normalized by performance on natural audio. Symbols follow those in Fig. 7c. c, Adversarial robustness of a set of adversarially trained visual models versus human recognizability of final-stage model metamers (N = 25 models). d, Operations included in the AlexNet architecture to more closely obey the sampling theorem (the resulting model is referred to as ‘LowpassAlexNet’). e, Schematic of VOneAlexNet. f, Adversarial vulnerability as assessed via accuracy on a 1,000-way ImageNet classification task with adversarial perturbations of different types and sizes. LowpassAlexNet and VOneAlexNet were equally robust to adversarial perturbations (F1,8 < 4.5, P > 0.1 and for all perturbation types), and both exhibited greater robustness than the standard model (F1,8 > 137.4, P < 0.031 and for all adversarial perturbation types for both architectures). Error bars plot s.e.m. across 5 random samples of 1,024 test images. g, Human recognition of model metamers from LowpassAlexNet, VOneAlexNet and standard AlexNet models. LowpassAlexNet had more recognizable metamers than VOneAlexNet (main effect of architecture: F1,19 = 71.7, P < 0.0001, ; interaction of architecture and model stage: F8,152 = 21.8, P < 0.0001, ). Error bars plot s.e.m. across participants (N = 20). h, Example model metamers from the experiment in d. i, Schematic depiction of how adversarial vulnerability could dissociate from human recognizability of metamers. j, Example augmentations applied to images in tests of out-of-distribution robustness. k, Scatter plot of out-of-distribution robustness versus human recognizability of final-stage model metamers (N = 26 models). Models with large-scale training are denoted with ★ symbols. Other symbols follow those in Fig. 7a; the abscissa value is a single number, and error bars for ordinate represent s.e.m. across participants.