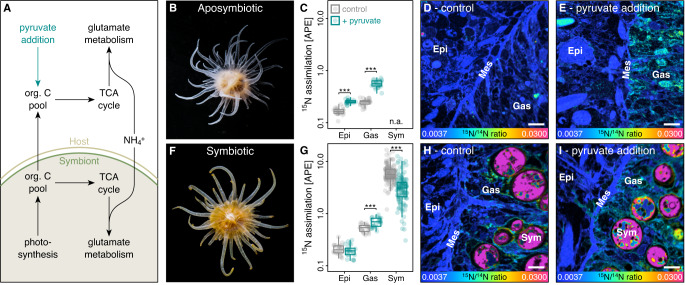
Fig. 1. Effects of labile carbon availability on ammonium (NH4+) assimilation in Aiptasia.
A Amino acid synthesis by the host and its algal symbionts links carbon and nitrogen cycling in the symbiosis. B Aposymbiotic Aiptasia were used to quantify (C) the effect of 10 mM pyruvate addition on light 15NH4+ assimilation in host tissue layers using (D, E) NanoSIMS imaging. Likewise, (F) symbiotic Aiptasia were used to quantify (G) the effect of 10 mM pyruvate addition on light 15NH4+ assimilation in the host tissue layers as well as algal symbiont cells using (H, I) NanoSIMS imaging. Scale bars are 5 µm. Boxplots indicate median, upper and lower quartiles, whiskers show 1.5 × interquartile range. inter Asterisks indicate significant effects of pyruvate addition on 15N assimilation in the specific tissue or cell (***p < 0.001). 24 host epidermis, 24 host gastrodermis, and 40 algal symbiont regions of interest from three Aiptasia were analyzed per treatment condition for aposymbiotic and symbiotic Aiptasia, respectively. APE atom % excess relative to unlabeled controls, Epi host epithelium, Gas host gastrodermis, Mes host mesoglea, Sym algal symbionts. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.