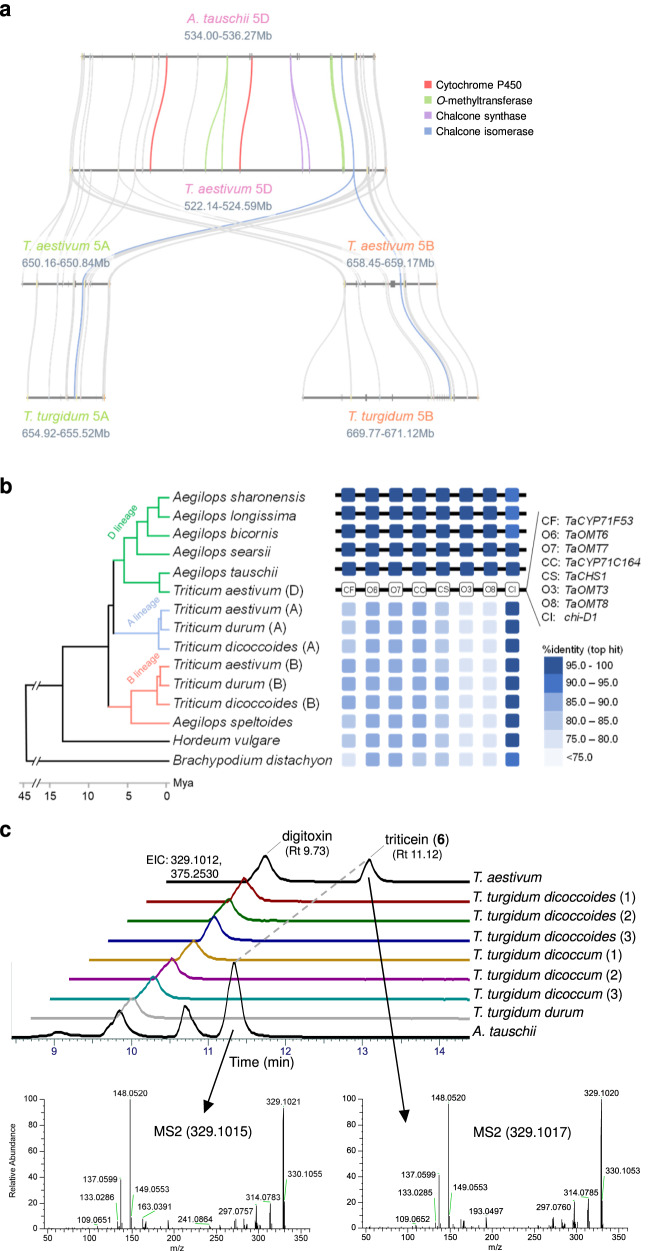
Fig. 5. Occurrence of triticein gene cluster in wheat and other cereal genomes.
a Microsynteny analysis of triticein BGC in wheat group 5 chromosomes, and syntenic regions in Aegilops tauschii and wild emmer wheat (T. turgidum). b The triticein BGC is conserved in Aegilops tauschii and four Aegilops grasses from section Sitopsis, but absent in A and B lineage genomes, including wild emmer wheat (T. turgidum ssp. dicoccoides), durum wheat (T. turgidum ssp. durum), and putative B genome progenitor, Aegilops speltoides. Color coding shows % identity of nucleotide sequence of top blastn alignment with the coding sequences of the respective BGC4(5D) genes. The phylogenetic tree is adapted from Li et al.36. c Extracted ion chromatogram (EIC) and MS2 fragmentation for triticein (m/z = 329.1012) in bread wheat, emmer wheat and Aegilops tauschii. Digitoxin (m/z = 375.2530) was used as an internal standard. Y-axes of all chromatograms are linked. Cultivars/accessions analyzed, in order shown in figure from top to bottom: T. aestivum Cadenza; T. turgidum TRI 18539, PI 428127, PI 466991, CGN 16073, CGN21064, TRI 6141, Miradoux; A. tauschii subsp. strangulata TOWWC0190.