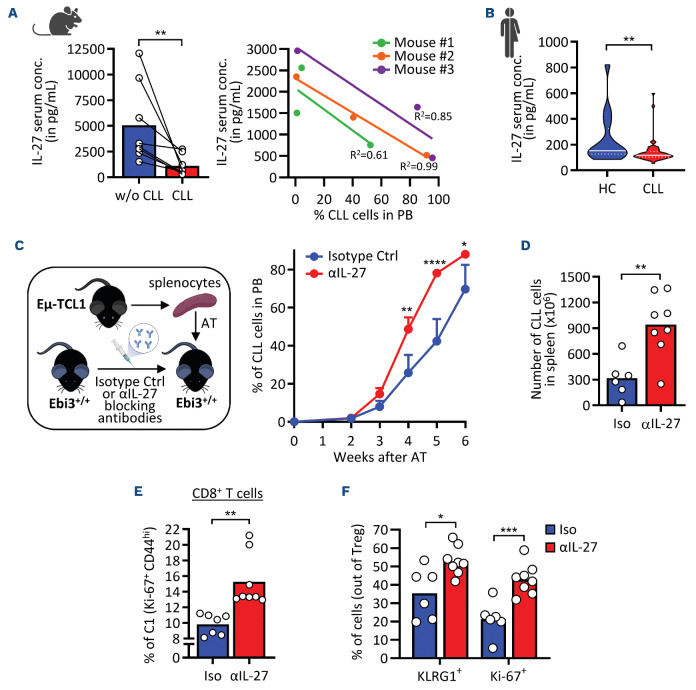
Figure 6.
IL-27 level is reduced in the blood of leukemic mice and chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients and IL-27 neutralization enhanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia development as observed in Ebi3-/- mice. (A) (Left) Serum levels of interleukin 27 (IL-27) in mice before and after chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) development. (Right) Correlation between IL-27 serum levels and CLL development in mice measured by enzyme-linked immosorbant assay (ELISA). (B) Serum levels of IL-27 in CLL patients (N=53) and healthy controls (N=16) measured by ELISA. (C-F) (Right) A cohort of recipient Ctrl mice was intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected with α-IL-27 or isotype control antibodies and subsequently adoptively transferred with splenocytes from leukemic Eμ-TCL1 mice. Mice were bled weekly to evaluate peripheral disease development. The injection of antibodies was maintained once per week until euthanasia. (C) (Left) Percentages of circulating leukemic CD5+ CD19+ cells in the 2 groups (N=7 for isotype group and N=8 for α-IL-27 group, two-way ANOVA test. (D-F) Mice were euthanized and their splenocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Number of CLL cells in the spleen of both experimental conditions. (E) Distribution of cells in cluster C1 among CD8+ T cells from isotype- and α-IL-27-treated mice. (F) Percentage of KLRG1+ or Ki67+ Treg from isotype- and α-IL-27-treated mice. Unpaired t test, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.