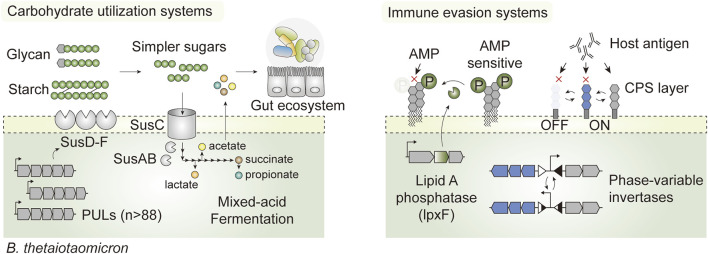
FIGURE 4.
Hallmark features that promote in vivo survival in the prominent gut commensal Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. The presence of exhaustive carbohydrate-active enzymes encoded by PULs enables foraging on complex dietary carbohydrates and host glycans (Starch utilization systems; SusA-F for illustration purposes). This not only confers a competitive edge for survival through the feast and famine cycles in the intestine, but it also shapes the luminal nutrient (or metabolic) landscape by converting otherwise inaccessible carbohydrates into simpler oligosaccharides and short chain fatty acids that can be utilized by the native gut flora and host epithelia. B. thetaiotaomicron also houses phase variable invertases and phosphatases that dynamically shift cell surface architectures in response to environmental perturbation, promoting evasion of the host immune system and exogenous antimicrobial peptides (AMP).