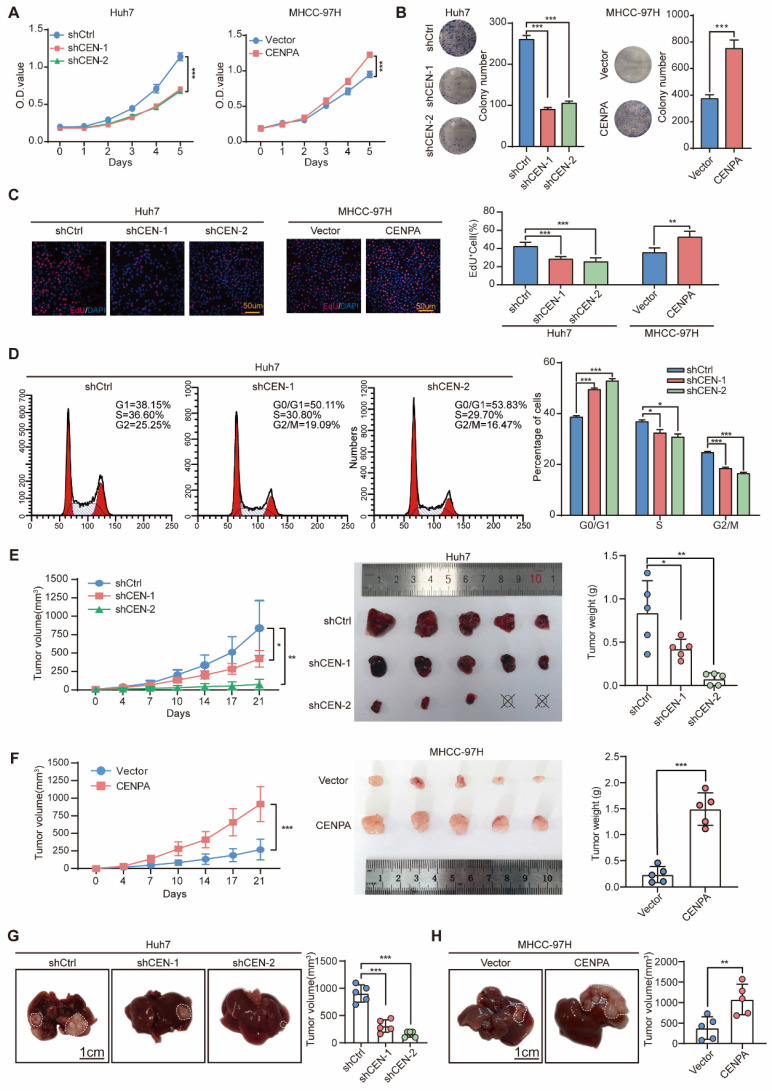
Figure 2.
CENPA promotes HCC cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. (A) CCK-8 assay of Huh7 and MHCC-97H cells after CENPA knockdown or overexpression. (B) Clone formation assays of Huh7 and MHCC-97H cells after CENPA knockdown or overexpression. (C) Representative images of EdU assays and quantification of EdU+ cells in CENPA knockdown or overexpression cells. (D) Statistical analysis revealed the cell cycle changes after CENPA knockdown in Huh7 cells. (E) Subcutaneous tumor growth assay in mice injected with CENPA knockdown Huh7 cells. Growth curves and weight of subcutaneous tumor in the indicated groups (n=5 mice/group). (F) Subcutaneous tumor growth assay in mice injected with CENPA overexpression in MHCC-97H cells. Growth curves and weight of subcutaneous tumor in the indicated groups (n=5 mice/group). (G) Representative tumor images and tumor volumes after CENPA knockdown in the orthotopic Huh7 cell model. (H) Representative tumor images and tumor volumes after CENPA overexpression in the orthotopic MHCC-97H cell model. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 3 independent experiments. The statistical significance was determined by Student's two-tailed t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. OD optical density.