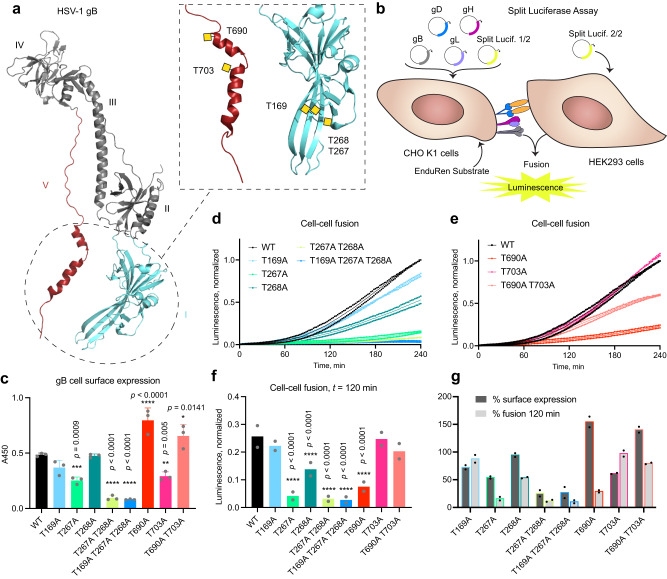
Fig. 6. Single O-glycosites affect gB-mediated cell-cell fusion efficiency.
a HSV-1 gB structure (PDB: 2GUM) with select mutated O-glycan acceptor sites indicated within the dashed box. Respective previously identified O-glycans were drawn manually as yellow squares. Domains are numbered in roman numericals according to Heldwein et al., Science 2006. b The cartoon illustrates the principle of split luciferase assay. c Cell surface expression of gB O-glycosite Thr to Ala mutants evaluated by CELISA using mouse anti-gB antibodies. Data is shown as mean absorbance at 450 nm + SD of three technical replicates and is representative of three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test was used to evaluate differences from WT (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). d, e Cell-cell fusion activity over 240 min using gB O-glycosite Thr to Ala mutants. Data from two independent experiments is shown, where mean normalized luminescence of three technical replicates at each time point is indicated by a dot. Mean values of the two independent experiments are shown as thin lines. Data is normalized to maximum luminescence reading at final time point using WT gB for each experiment. d Data related to gB domain I mutations. e Data related to gB domain V mutations. f Cell-cell fusion activity of gB mutants at t = 120 min. Data is shown as mean normalized luminescence from two independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test was used to evaluate differences from WT (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). g Average percentages of cell surface expression and fusion efficiency at t = 120 min from two independent experiments are shown in side-by-side columns. Source data are provided as a Source Data file for all graphs.