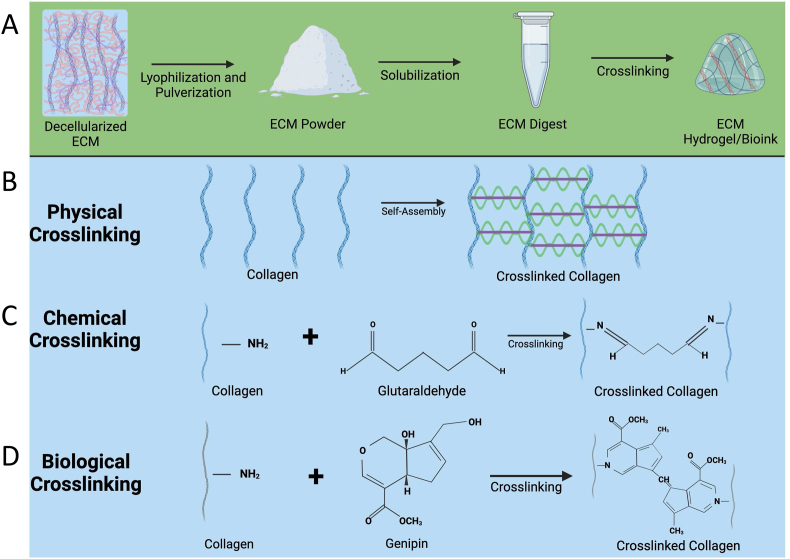
Fig. 2.
Development of dECM hydrogels/bio-inks. In the schematic representation (A), decellularized tissue undergoes a series of processing steps to form hydrogels/bio-inks. Initially, the tissue is decellularized, followed by conversion into a powder form. Subsequently, the powder is solubilized and digested to obtain dECM hydrogel. Cross-linking of dECM is essential to maintain mechanical strength and the stability of the structure in a biological environment. Different crosslinking methods can be employed for dECM cross-linking, as illustrated in panels (B), (C), and (D). Physical crosslinking (B) involves self-assembly under physiological conditions. Chemical crosslinking (C) can be achieved using agents like Glutaraldehyde. Biological/enzymatic crosslinking (D) can be facilitated using biological agents or naturally available materials such as genipin.