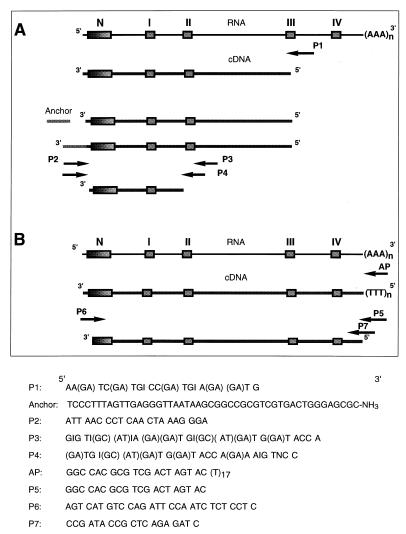
FIG. 1.
Strategy used for PCR cloning of the laccase-encoding cDNA from P. cinnabarinus and oligonucleotide primer sequences. The boxes indicate the regions encoding the N terminus of the mature protein and the Cu(II)-binding regions of the laccase that are highly conserved in blue copper oxidases. (A) Results of laccase-specific reverse transcription of P. cinnabarinus RNA and anchor-ligated PCR used to amplify the 450-bp fragment of the P. cinnabarinus laccase cDNA on which the gene-specific primer P6 was based. (B) After primer AP-primed reverse transcription of full-length P. cinnabarinus mRNAs, primer P5 was used in conjunction with primer P6 to amplify the laccase-encoding sequence. Primers P6 and P7 were used to clone the genomic laccase sequence.