Fig. 2.
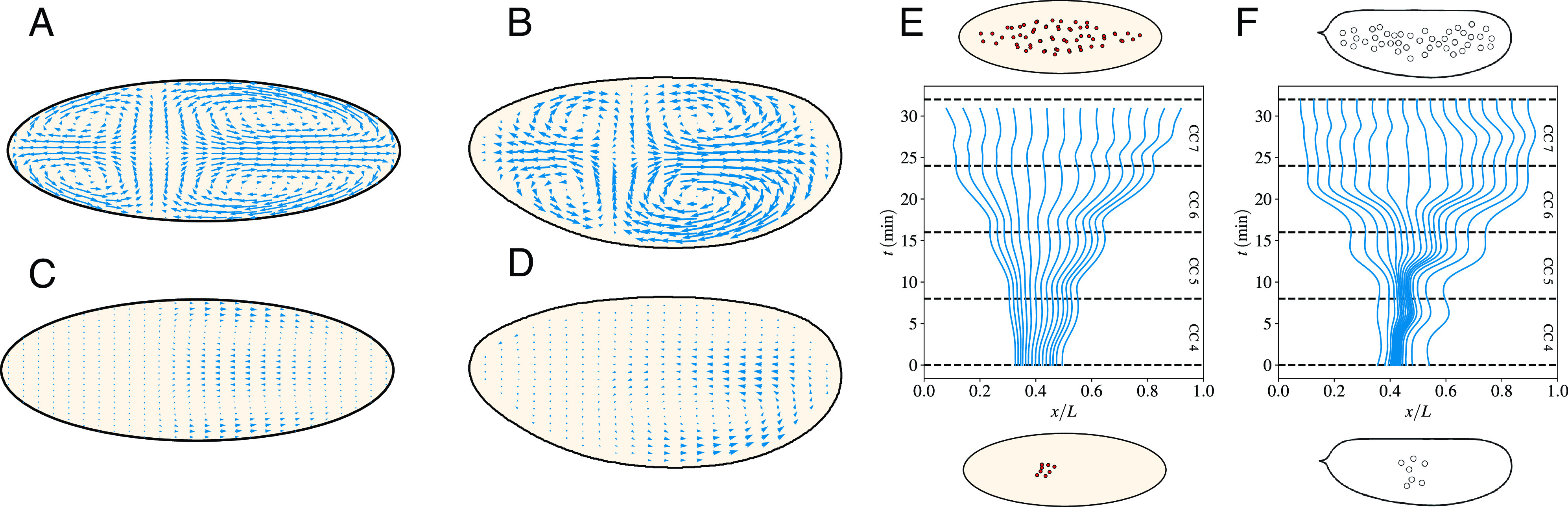
The two-fluid model captures the large-scale feature of embryonic flows. (A) and (B) Typical cytoplasmic flow observed during the AP expansion phase in our model (A) and experiments (B). (C) and (D) Typical cytoplasmic backflow observed during the AP contraction phase in our model (C) and experiments (D). The length of the arrows is in the same units as in panel (A and B) so as to highlight the reduced speed of backflow. (E) and F) Reconstructed initial distributions to achieve a uniform nuclear distribution at the end of cell cycle 7 in our model (E) and wild-type experiments (F). Particles are uniformly distributed along the AP axis at the end of cycle 7 and simulated (E) or measured (F) cytoplasmic flows are used to evolve their position backward in time until the beginning of cycle 4.
