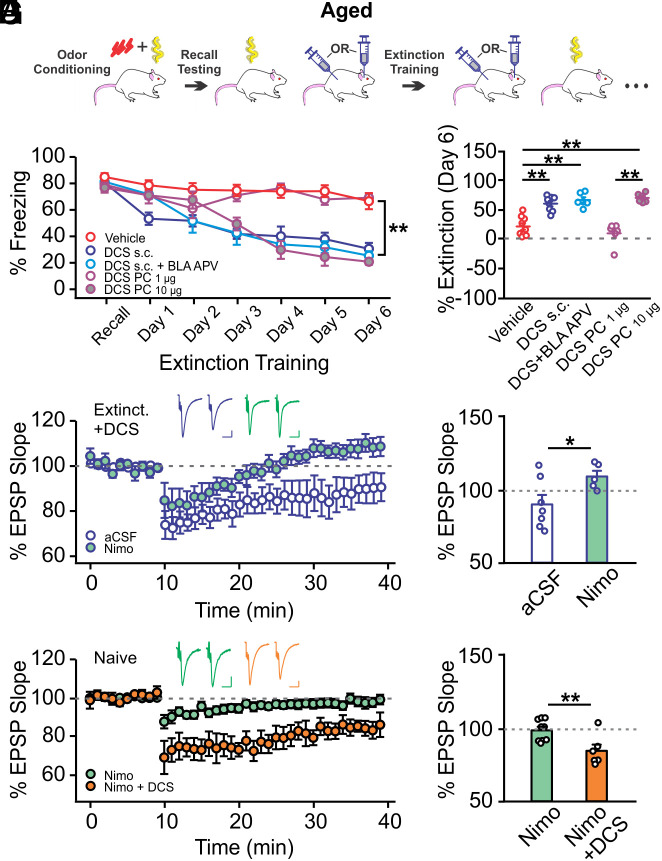
Fig. 4.
NMDAR activation in the PC restores olfactory threat extinction in aged rats. (A) Schematic of olfactory threat conditioning and extinction training. (B) Extinction learning curves in rats injected with D-cycloserine (DCS) or vehicle during extinction training (n = 9/8/6/6/6 for vehicle/DCS s.c./DCS s.c.+BLA APV/DCS PC 1 µg/DCS PC 10 µg). Systemic injection or PC infusion (10 µg) of DCS rescued extinction learning. (C) Comparisons of extinction levels of the groups in B. (D) LTD recordings of DCS-injected aged rats that underwent extinction training (n = 7 aCSF, n = 5 nimo). LTCC-dependent LTD was inducible in these rats. Nimo, nimodipine. (E) Comparisons of LTDs in aCSF and nimodipine groups in D. (F) LTD recordings in naive aged rats in the presence of nimo or nimo+DCS (n = 9 nimo, n = 6 nimo+DCS). The addition of DCS enabled LTD induction. (G) Comparisons of LTDs in the two groups in F. Scale bars for example fEPSP traces, 10 ms/0.2 mV. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.