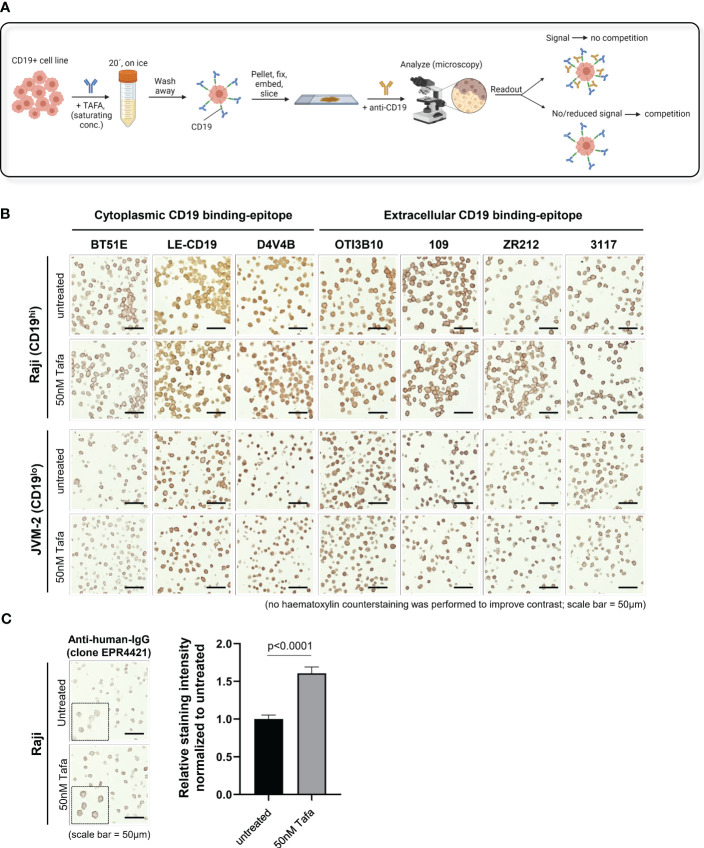
Figure 1.
CD19 can be detected by IHC using commercial antibodies independent of tafasitamab pretreatment. (A) Schematic of an IHC workflow designed to assess TAFA competition with commercial anti-CD19 antibody clones for IHC. CD19+ cell lines were pre-incubated with saturating concentrations of TAFA (50 nM), washed, and processed to form a cell pellet. The pellets were formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE), sectioned, and stained with commercial anti-CD19 antibodies. Competition was confirmed when a reduction in signal was observed on TAFA pre-treated samples. Schematic was created using BioRender.com. (B) IHC competition experiments. Raji and JVM-2 cells were processed as described above. CD19 detection antibodies against the cytoplasmic tail of CD19 (clones BT51E, LE-CD19, D4V4B) and the extracellular domain of CD19 (clones OTI3B10, 109, ZR212, 3117) were tested. Samples were analyzed using the following equipment/parameters: Axiolab 5 microscope, Zeiss Axiocam 208 color camera, Zeiss N-Achroplan objective, magnification = 40x, numerical aperture = 0.65, at room temperature. Images were processed using the Zeiss Axiocam 208 color camera built-in software (firmware version 1.3.6) (C) To confirm that TAFA is still present in the FFPE samples and not lost during cell pellet processing, untreated and TAFA pre-treated samples were stained with anti-human IgG. Sample acquisition and analysis specifics were as described above. Quantification was performed with 30 cells per condition and relative staining intensity normalized to untreated cells is shown. Statistical analysis: Mann-Whitney test.