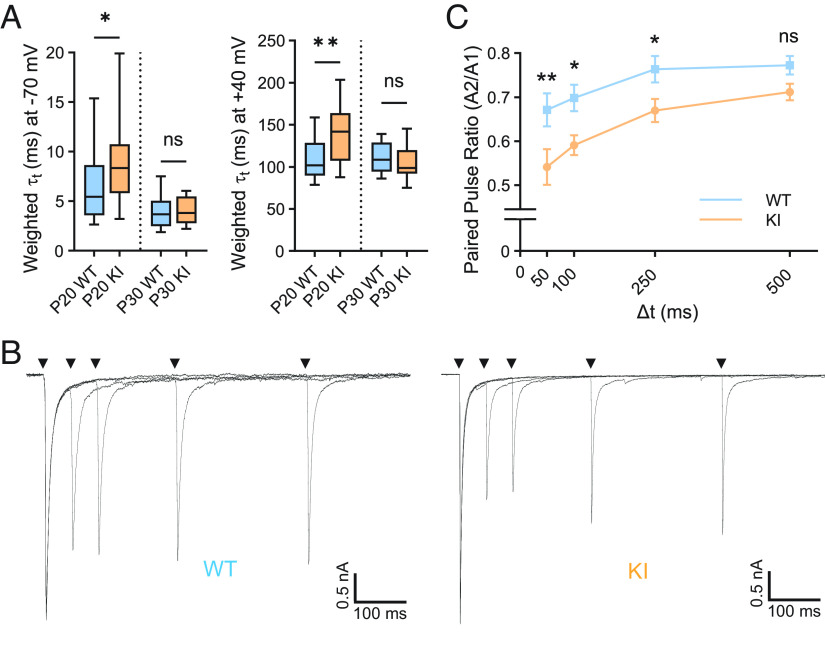
Fig. 4.
Retinogeniculate synaptic properties are altered in QKI mice. (A) Decay kinetics of EPSCs at −70 mV (Left) and +40 mV (Right) are significantly slower in QKI at P20, but not at P30, as compared to WT mice. (B) Superimposed pairs of EPSCs recorded at a holding potential of −70 mV with varying ISIs (50, 100, 250, and 500 ms) from P29-32 WT (Left) and QKI (Right) mice. Stimulus artifacts were blanked for clarity. (C) Mean paired pulse ratio (PPR) ± SEM, calculated by dividing the amplitude of the second EPSC (A2) by the amplitude of the first EPSC (A1), shows greater short-term depression in QKI mice as compared to WT mice at three interstimulus intervals (ISIs) tested. WT: n = 17 from three mice; KI: n = 14 cells from four mice. Statistics in (A) were performed using a two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test, and those in (B) using a one-way ANOVA and Fisher’s LSD of multiple comparisons. ns, P > 0.05; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.