Abstract
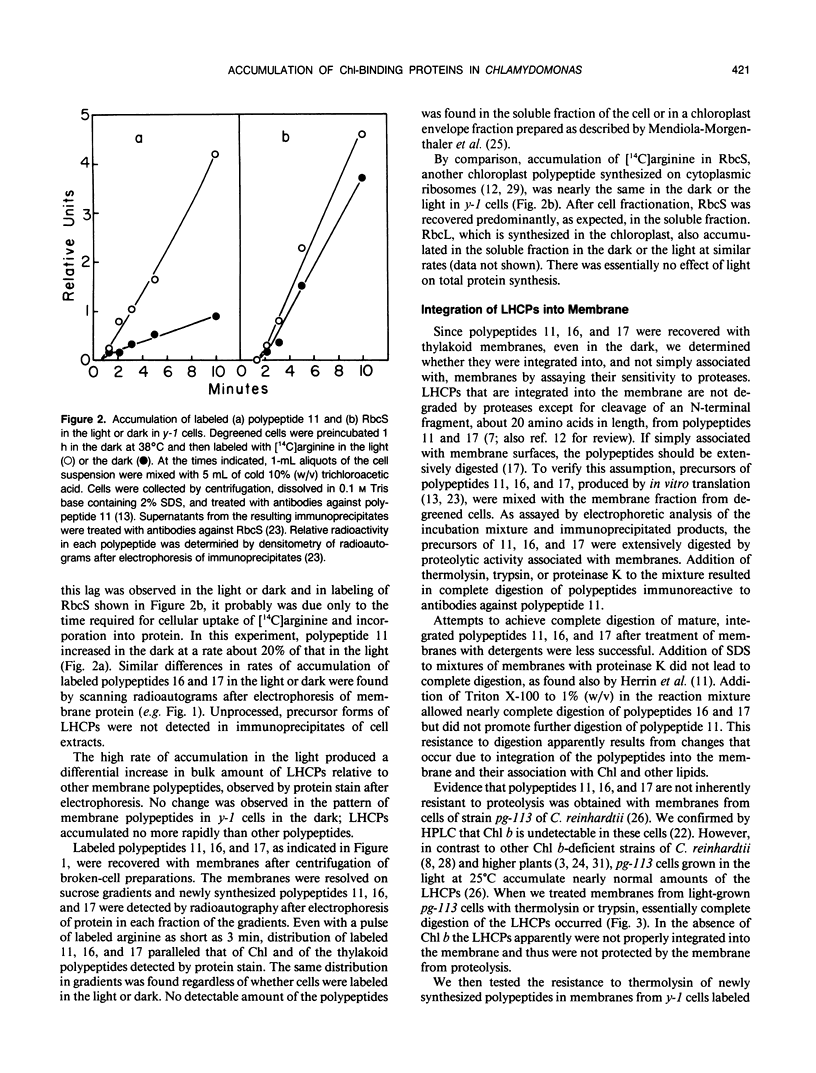
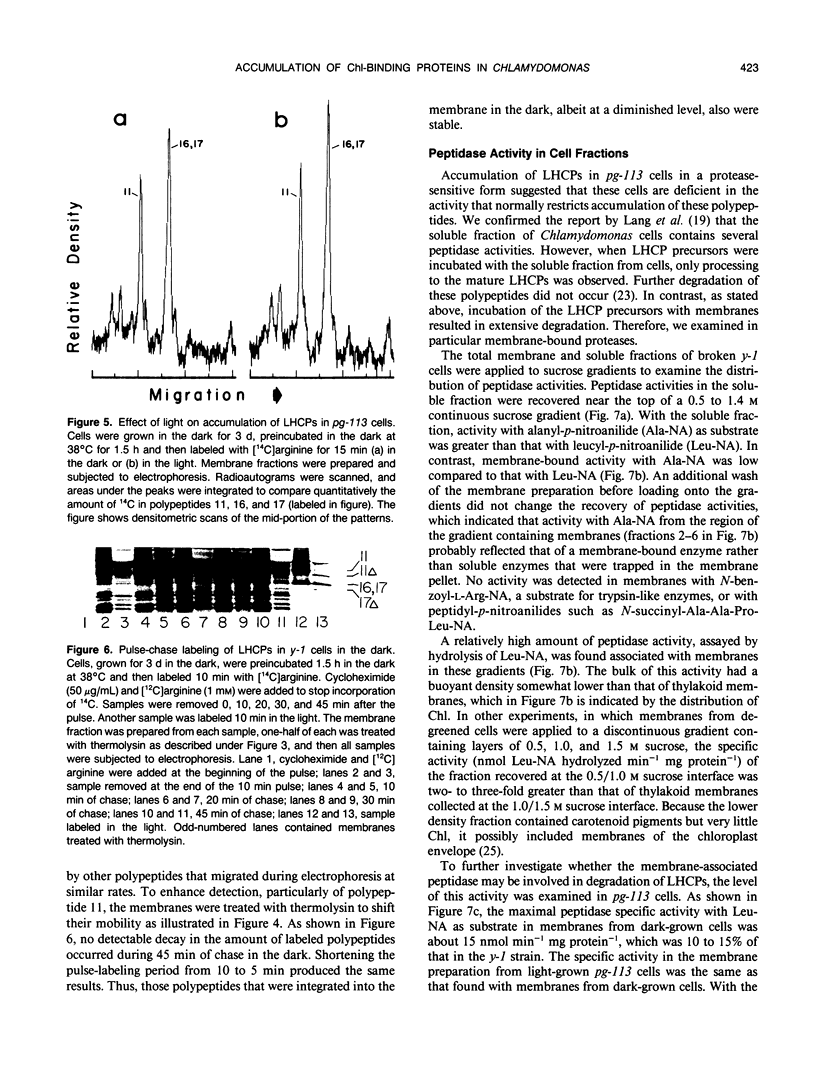
The kinetics of accumulation of light harvesting chlorophyll (Chl) a/b-binding polypeptides (LHCPs) in thylakoid membranes were analyzed during greening of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii y-1 at 38°C. Initial accumulation of LHCPs in thylakoid membranes was linear; LHCP precursors or polypeptides in transit within the chloroplast stroma were not detected. The rate of accumulation in the light was at least five-fold greater than that in the dark. The relatively small amount of LHCPs that accumulated in the dark was integrated properly in the membrane, as judged by the pattern of cleavage in vitro by exogenous proteases, and did not turn over at a significant rate in vivo. The kinetic data suggested that in y-1 cells either translation of LHCP mRNA was inhibited in the dark or newly synthesized polypeptides were degraded concurrently with transport into the chloroplast unless rescued by Chl. LHCPs accumulated in cells of the Chl b-deficient strain pg-113 at the same rate in the dark or the light at 38°C, an indication that light did not affect translation of LHCP mRNA. Membrane-associated LHCPs in pg-113 cells were completely degraded, in contrast to those in y-1 cells, by exogenous proteases, which suggested that pg-113 cells are deficient in a proteolytic activity. A peptidase was recovered from y-1 cells in a membrane fraction with a buoyant density slightly less than that of thylakoid membranes. Although a role for this activity in degradation of LHCPs has not been established, the specific activity of this peptidase in pg-113 cells was only 10 to 15% of the level in y-1 cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akoyunoglou A., Akoyunoglou G. Reorganization of Thylakoid Components during Chloroplast Development in Higher Plants after Transfer to Darkness : Changes in Photosystem I Unit Components, and in Cytochromes. Plant Physiol. 1985 Oct;79(2):425–431. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarik D. P., Hoober J. K. Biosynthesis of a chlorophyllide b-like pigment in phenanthroline-treated Chlamydomonas reinhardtii y-1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jul;240(1):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare G., Bartlett S. G., Chua N. H. Biosynthesis of chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptides in wild type and the chlorina f2 mutant of barley. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7762–7767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. Regulation of photosynthesis by reversible phosphorylation of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 15;212(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2120001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Bennoun P. Thylakoid membrane polypeptides of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: wild-type and mutant strains deficient in photosystem II reaction center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Blomberg F. Immunochemical studies of thylakoid membrane polypeptides from spinach and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. A modified procedure for crossed immunoelectrophoresis of dodecyl sulfate.protein complexes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Fulsom D. R., Viitanen P. V. An imported thylakoid protein accumulates in the stroma when insertion into thylakoids is inhibited. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14225–14232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K. Light-Harvesting Chlorophyll a/b Protein : Membrane Insertion, Proteolytic Processing, Assembly into LHC II, and Localization to Appressed Membranes Occurs in Chloroplast Lysates. Plant Physiol. 1988 Apr;86(4):1120–1126. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin D. L., Plumley F. G., Ikeuchi M., Michaels A. S., Schmidt G. W. Chlorophyll antenna proteins of photosystem I: topology, synthesis, and regulation of the 20-kDa subunit of Chlamydomonas light-harvesting complex of photosystem I. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 May 1;254(2):397–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Marks D. B., Keller B. J., Margulies M. M. Regulation of accumulation of the major thylakoid polypeptides in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii y-1 at 25 degrees C and 38 degrees C. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):552–558. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Millington R. H., D'Angelo L. P. Structural similarities between the major polypeptides of thylakoid membranes from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jun;202(1):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Stegeman W. J. Kinetics and regulation of synthesis of the major polypeptides of thylakoid membranes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii y-1 at elevated temperatures. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):326–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Harel E., Chitnis P. R., Thornber J. P., Tobin E. M. Functional and mutational analysis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of thylakoid membranes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):972–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Tobin E. M. A hydrophobic, carboxy-proximal region of a light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein is necessary for stable integration into thylakoid membranes. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):159–166. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchka M. R., Mayfield S. P., Rochaix J. D. Nuclear mutations specifically affect the synthesis and/or degradation of the chloroplast-encoded D2 polypeptide of photosystem II in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):319–324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Jagendorf A. T. Neutral peptidases in the stroma of pea chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):603–608. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnoë P., Mayfield S. P., Rochaix J. D. Comparative analysis of the biogenesis of photosystem II in the wild-type and Y-1 mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):609–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney M. A., Hoober J. K., Marks D. B. Kinetics of Chlorophyll Accumulation and Formation of Chlorophyll-Protein Complexes during Greening of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii y-1 at 38 degrees C. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):1100–1106. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks D. B., Keller B. J., Hoober J. K. In Vitro Processing of Precursors of Thylakoid Membrane Proteins of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii y-1. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):108–113. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell J. P., Webber A. N., Lake B. Mutants of Sweetclover (Melilotus alba) Lacking Chlorophyll b: Studies on Pigment-Protein Complexes and Thylakoid Protein Phosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):948–951. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Import of proteins into mitochondria: a multi-step process. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):205–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselet A., Wollman F. A. Protein rotational mobility in thylakoid membranes of different polypeptide composition in the wild type and mutant strains of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Apr;246(1):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90477-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Mishkind M. L. Rapid degradation of unassembled ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunits in chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Timberg R., Ohad I. Turnover of thylakoid photosystem II proteins during photoinhibition of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUPPY H., WIESBAUER U., WINTERSBERGER E. [Amino acid-p-nitroanilide as a substrate for aminopeptidases and other proteolytic enzymes]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1962 Nov 15;329:278–288. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1962.329.1.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]