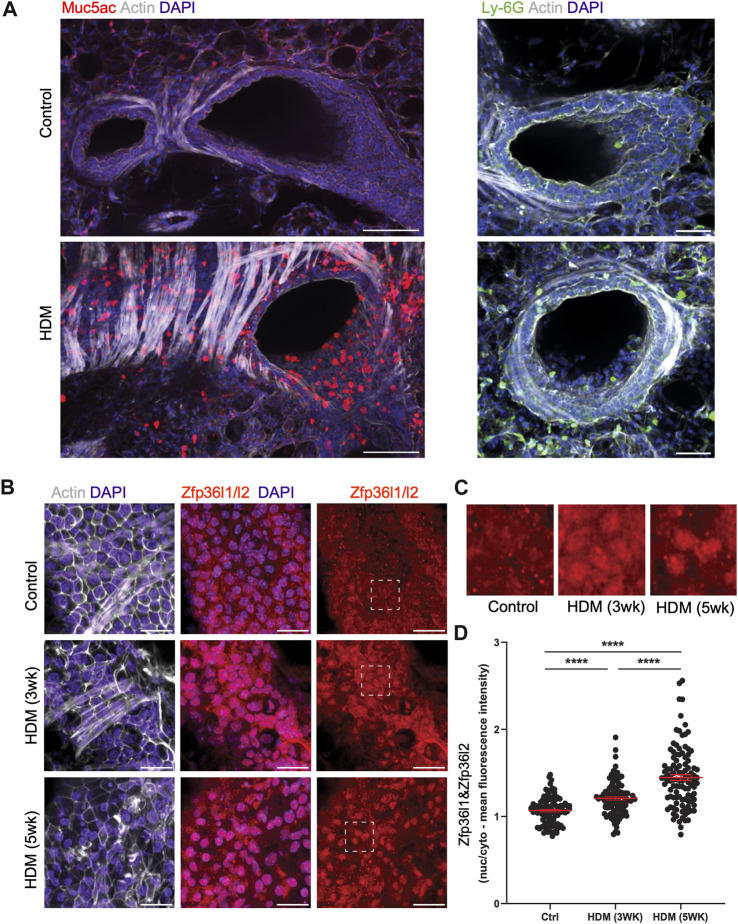
FIGURE 4.
Intracellular mislocalization of Zfp36l1/Zfp36l2 in airway epithelial cells of mice with asthma-like characteristics. (A) Representative spinning disc confocal images of ex vivo lung slices from healthy controls and HDM-treated (3 weeks) mice were fixed and immune-stained for asthmatic markers of mucus (Muc5ac) and neutrophils (Ly-6G) to demonstrate an asthma phenotype (scale bars are 100 and 50 microns, respectively). (B) Confocal projections of healthy and HDM-treated airway epithelial cells immune-stained for Zfp36l1/l2, actin and nuclei (scale bar 25 microns), with insets highlighting Zfp36l1/Zfp36l2 intracellular localization in epithelial cells in health (Control), HDM after 3 weeks of exposure (HDM 3 weeks) and after 5 weeks of exposure (HDM 5 weeks). (C): Insets highlighting its nuclear accumulation of Zfp36l1/l2 in epithelial cells in HDM. (D) Quantification of nuclear and cytoplasmic mean fluorescence intensity of Zfp36l1/Zfp36l2 in control and HDM-treated airways (3 weeks and 5 weeks of exposure), using regions of interest (ROIs) defined by the DAPI (nuclei) and actin (cytoplasm) channels. Mann-Whitney test was performed on 100 cells from 3 mice per group. ****: p < 0.0001. Ctrl: Control. HDM: House dust mite.