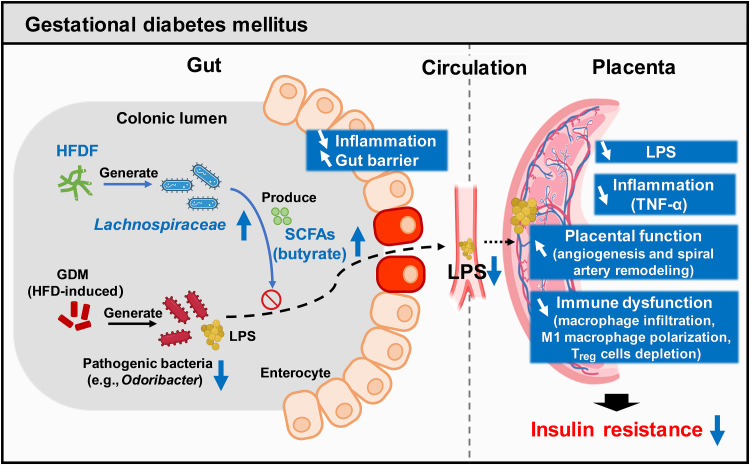
Fig. 9. GDM is associated with the development of placental hypofunction and inflammation.
A HFDF (konjac) could reduce GDM development through gut-SCFA-placenta axis in the GDM mouse model. Mechanistically, the HFDF could increase the abundances of Lachnospiraceae and butyrate, enabling the reduction of placental-derived inflammation by enhancing gut barrier and inhibiting the transfer of bacterial components (LPS), ultimately resisting HFD-induced insulin resistance. Lachnospiraceae and butyrate have similar anti-GDM and anti–placental inflammation effects, and they can ameliorate placental function and pregnancy outcomes probably by dampening placental immune dysfunction.