Figure 1. Assembly, control, and functional properties of robotic nanozyme assemblies and their mode of action.
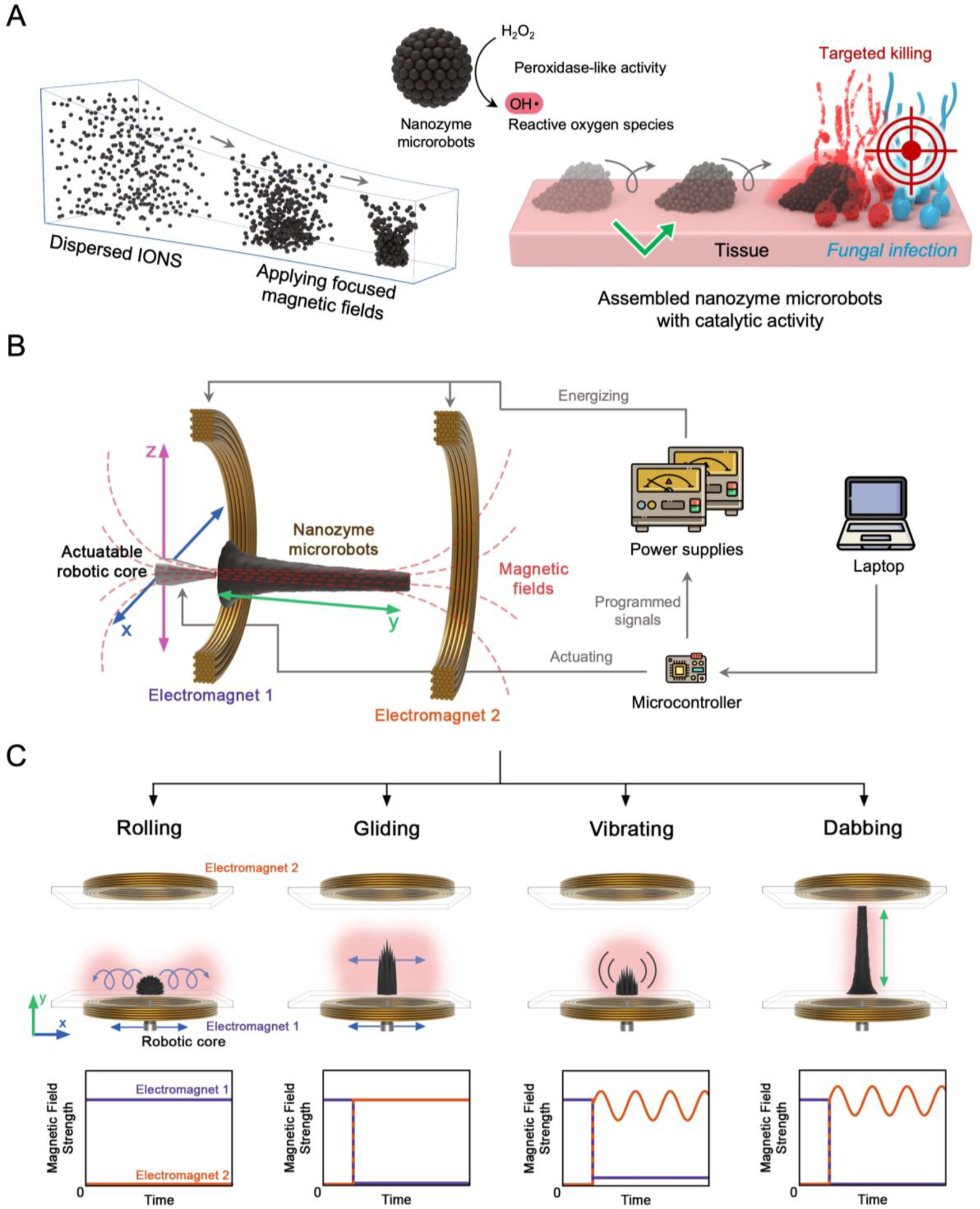
(A) On-site assembly of individual nanozymes into catalytically active superstructures. The motion dynamics, morphology, and the location of catalysis of the structured assemblies can be controlled creating nanozyme microrobots for targeting fungal infection. (B) Electromagnet cores guide the nanozyme microrobot assemblies with controllable morphology, position, and motion using programmed algorithms. (C) Programmable dynamic motions via magnetic field modulation enable controlled catalytic activities and targeted treatment.
