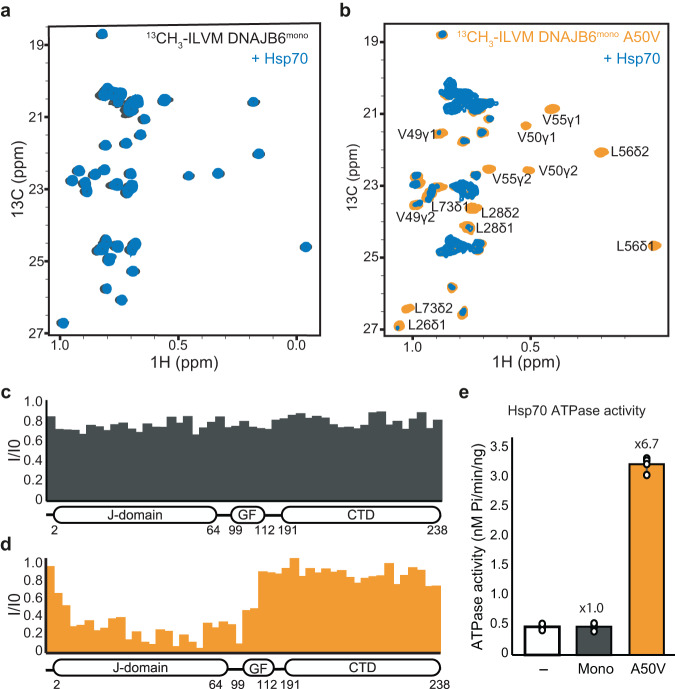
Fig. 5. Interaction of monomeric DNAJB6 variants with Hsp70.
a 13C-1H HSQC spectra of monomeric DNAJB6 (DNAJB6 ΔST) alone (gray), and in the presence of 2-fold excess of Hsp70 (blue). No binding is detected between Hsp70 and WT DNAJB6. b 13C-1H HSQC spectra of monomeric DNAJB6 A50V mutant alone (orange), and in the presence of a 2-fold excess of Hsp70 (blue). Significant changes to the DNAJB6 A50V spectrum were observed upon the addition of Hsp70, indicating binding. c, d Methyl-group peak intensity ratios (Ibound/Ifree) of monomeric WT DNAJB6 (c) or A50V mutant (d), upon addition of Hsp70. Hsp70 caused considerable reductions in the intensity of the J-domain residues of the DNAJB6 A50V mutant, while no binding was detected with the WT protein. e Steady-state ATPase activity of Hsp70 alone (white) and upon incubation with monomeric WT DNAJB6 or A50V disease mutant. The WT shows no activation of Hsp70 ATPase activity, while the A50V mutant enhances the activity 6.7-fold. Data are means ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments).