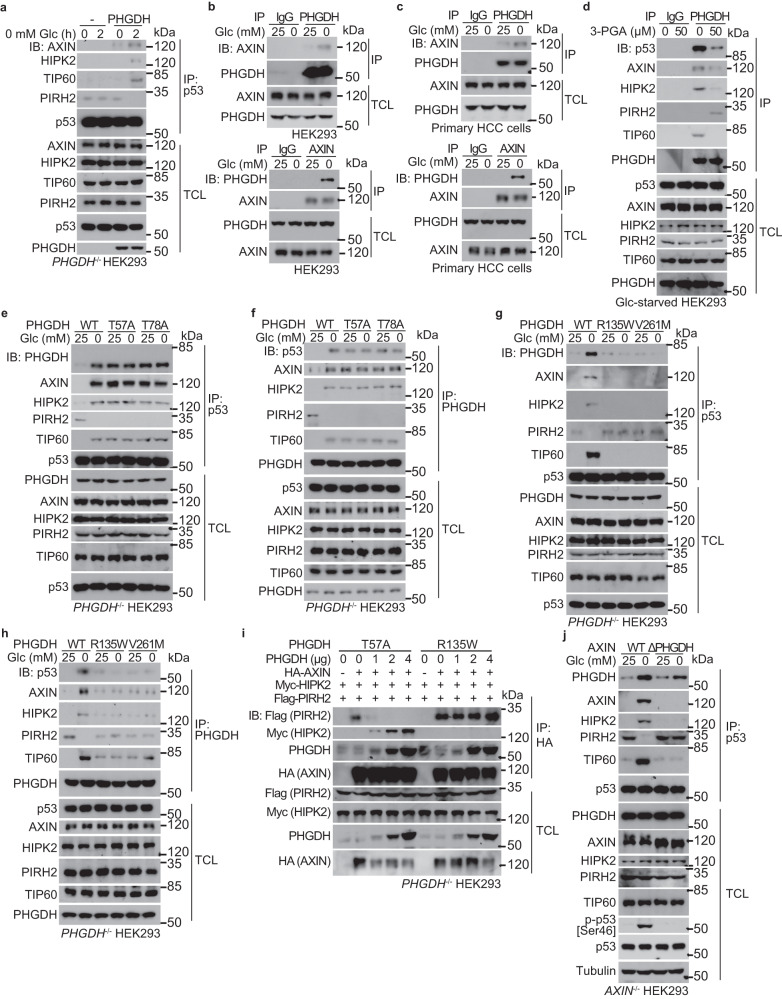
Fig. 3. 3-PGA-unoccupied PHGDH promotes the formation of PHGDH–AXIN–HIPK2–p53 complex.
a PHGDH is required for the low glucose-induced complex formation with AXIN–HIPK2–p53 complex. PHGDH–/– HEK293 cells were re-introduced with PHGDH or vector control, and were glucose starved for 2 h, followed by immunoprecipitation of endogenous p53 and immunoblotting with antibodies indicated. b, c Glucose starvation promotes the interaction between PHGDH and AXIN. HEK293 cells (b) or primary human HCC cells (c) were regularly cultured, or were glucose starved for 2 h, followed by immunoprecipitation of endogenous PHGDH (upper panel) or AXIN (lower panel) and immunoblotting for co-precipitated AXIN (upper panel) or PHGDH (lower panel). d 3-PGA dissociates the PHGDH–AXIN–HIPK2–p53 complex. The 2-h-glucose-starved HEK293 cells were lysed, followed by addition of 50 μM 3-PGA at indicated final concentrations into the lysates. Endogenous PHGDH was then immunoprecipitated, followed by immunoblotting. e–h Non-occupation of 3-PGA underlies the formation of PHGDH with AXIN–p53–HIPK2 complex. HEK293 cells with PHGDH knockout were re-introduced with PHGDH-T57A and PHGDH-T78A (e, f), or PHGDH-R135W and PHGDH-V261M (g, h), and were glucose starved for 2 h, followed by immunoprecipitation of endogenous p53 (e, g) or PHGDH (f, h). i The 3-PGA-unoccupied PHGDH dissociates PIRH2 from and recruits HIPK2 to AXIN. HEK293T cells were transfected with 2 μg of HA-tagged AXIN, 2 μg of FLAG-tagged PIRH2, 2 μg of FLAG-tagged HIPK2, along with FLAG-tagged PHGDH at indicated amounts. Cells were then lysed, followed by immunoprecipitation of HA-tag. j AXIN interaction with PHGDH is required for the formation of PHGDH–AXIN–HIPK2–p53 complex and phosphorylation of p53-Ser46 in low glucose. HEK293 cells with AXIN knockout were re-introduced with full-length AXIN or AXIN truncation mutant defective in binding to PHGDH (ΔPHGDH), and were glucose starved for 2 h, followed by analyses of proteins co-precipitated with p53, and of the levels of p-p53-Ser46. Experiments were performed three times.