Fig. 5.
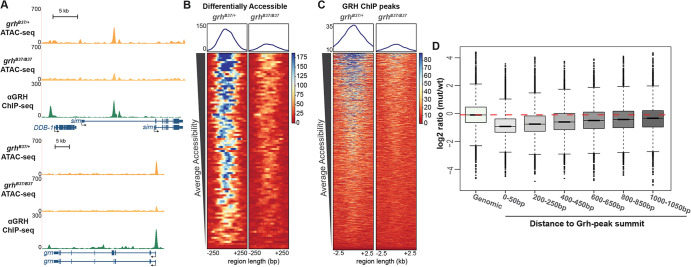
Grh is required for chromatin accessibility at 11-12 h AEL. (A) UCSC genome browser tracks of ATAC-seq from 11-12 h AEL for grh-null mutant embryos (grhB37/B37), stage-matched, wild-type sibling control (grhB37/+), and stage-matched Grh ChIP-seq (Nevil et al., 2017). (B) Heat maps of regions differentially accessible between the grh mutant and wild-type control. Color scale indicates relative height of ATAC-seq, i.e. accessibility. Heat maps are centered on ATAC-seq peak summits. (C) Heat maps of ATAC-seq data from grh-mutant and wild-type control embryos for all Grh-bound regions as identified by ChIP-seq. Color scale indicates relative height of ATAC-seq, i.e. accessibility. Heat maps are centered on Grh ChIP-seq peak summits. (D) Box plots of log2 ratios of ATAC-seq signal between grh-mutant and wild-type embryos, at windows of increasing distance around Grh ChIP-seq peak summits. Red dashed line indicates average signal of random genomic windows. Boxes represent the upper and lower quartiles around the median. Whiskers indicate the minimum and maximum, and outliers are represented as circles outside of the whiskers.