Figure 3.
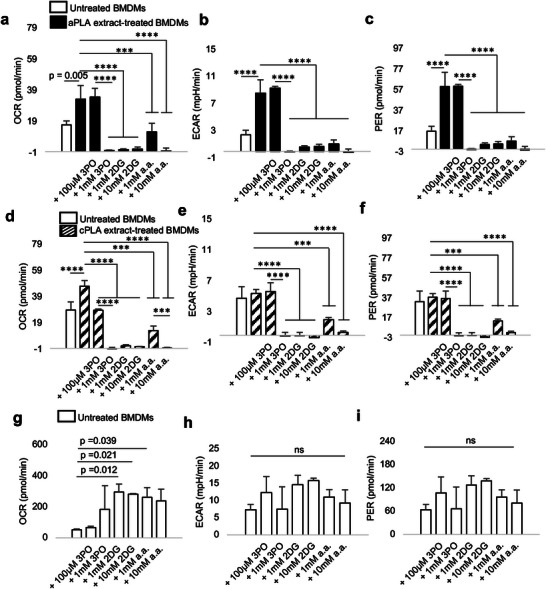
Functional metabolic indices are altered in primary bone marrow‐derived macrophages (BMDMs) after prolonged exposure to polylactide (PLA) degradation products (extract), and can be modulated by glycolytic inhibitors. a–c) Following exposure to amorphous PLA (aPLA) extract, oxygen consumption rate (OCR) (a) extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) (b) and proton efflux rate (PER) (c) are increased relative to controls, and this abnormal increase can be dose‐dependently controlled by various small molecule inhibitors. d–f) OCR (d) and not ECAR (e) and PER (f) are increased relative to controls in groups exposed to crystalline PLA (cPLA) extract, and functional metabolic indices can be controlled by pharmacologic inhibitors of glycolysis. g) Compensatory increase in OCR occurs in untreated BMDMs after treatment with some inhibitors. h,i) ECAR (h) and PER (i) are not affected by glycolytic inhibitors in untreated BMDMs. Not significant (ns), *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, mean (SD), n = 3, one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post‐hoc test; 3‐(3‐pyridinyl)−1‐(4‐pyridinyl)−2‐propen‐1‐ one (3PO), 2‐deoxyglucose (2DG) and aminooxyacetic acid (a.a.); 100 µl of control or PLA extract was used for 7 days.
