Fig. 3 |. Storage of memory in co-active neuronal networks, or engrams.
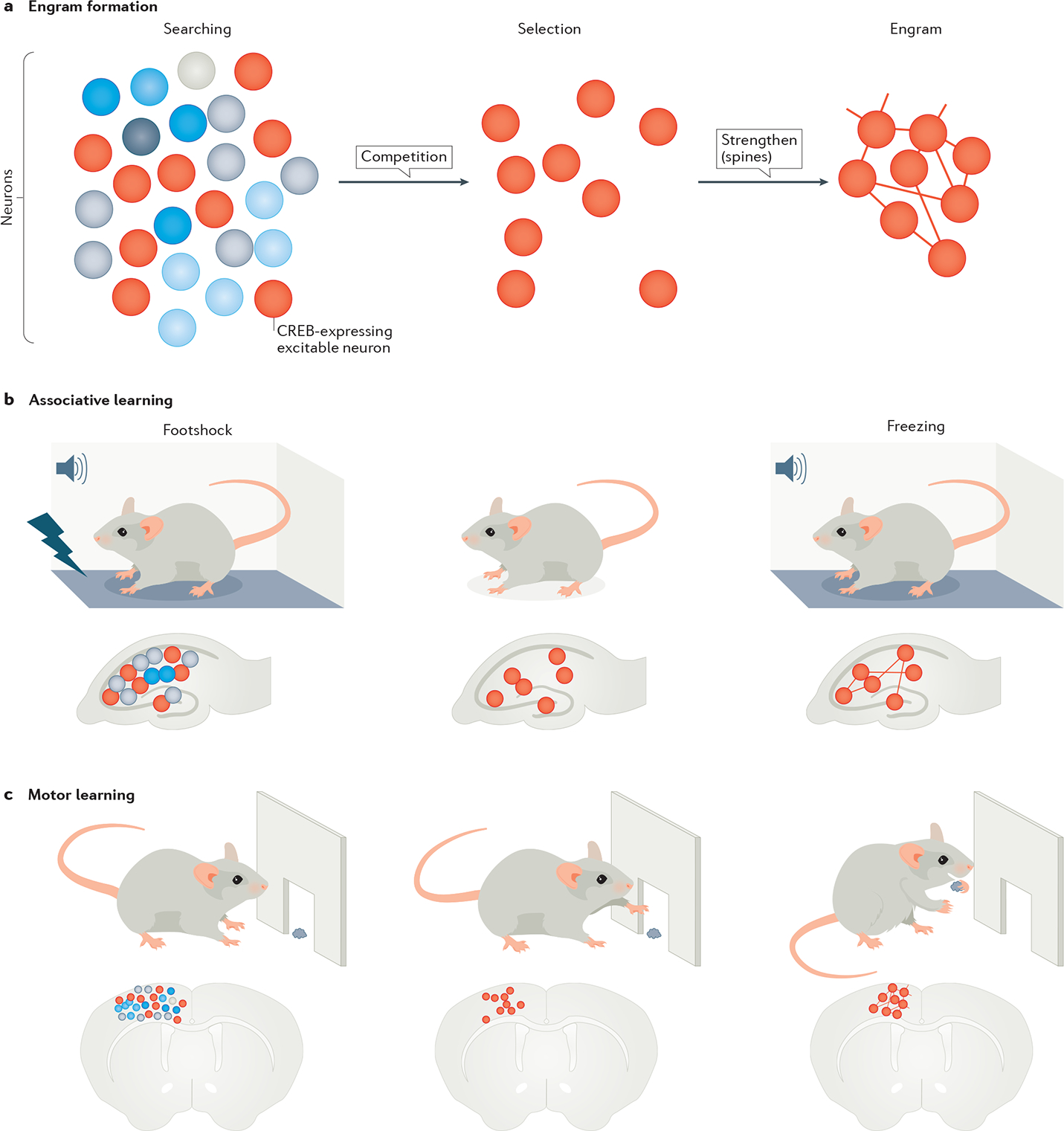
The figure shows the stages of engram formation that store a fear memory or motor memory. a | Engram formation begins with active searching for neurons that are co-active during a behavioural event. From this pool of neurons with similar spatiotemporal activation patterns, neurons with higher cAMP-binding response element (CREB) expression (red circles) are selected to form an engram. The connections within an engram are further strengthened through their dendritic spines that carry post-synaptic information. b | This part shows a collection of neurons in the hippocampus, with those showing CREB expression (red circles) storing a fear memory by associating foot shock with a tone. The fear memory can be recalled by reproducing the tone in the absence of shock and leads to freezing behaviour. The process of recall involves reactivating the memory engram associated with the foot shock. c | This part shows a similar engram in the motor cortex, which stores a motor skill as the motor task is being learnt. The learned function is allocated to a sparse and specific set of neurons initially selected from a large network.
