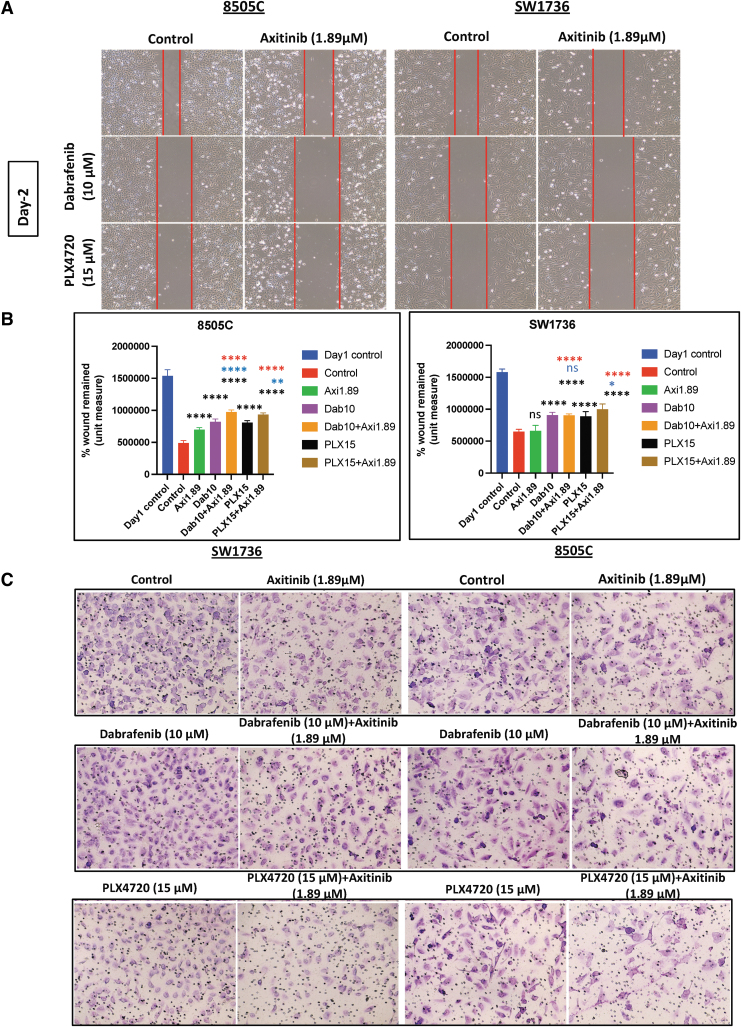
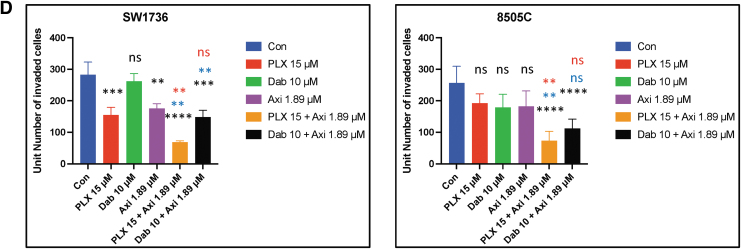
FIG. 2.
The combination of BRAF inhibition and axitinib treatment inhibits cell migration and invasion in BRAFV600E-mutant ATC cells. (A) The combination of PLX4720 (15 μM) and axitinib (1.89 μM) significantly inhibited cell migration compared with vehicle (p < 0.0001), PLX4720 (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05), and axitinib (p < 0.0001) in both cell lines. The combination of dabrafenib and axitinib significantly reduced cell migration compared with vehicle (p < 0.0001) and axitinib (p < 0.0001) in both cell lines 24 hours after scratching. (B) The histogram represents the mean wound area remaining 24 hours after scratching 8505C and SW1736 cells. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. (C) PLX4720 and axitinib treatment significantly reduced cell invasion after 24 hours compared with vehicle (p < 0.0001 and p < 0.001), PLX4720 (p < 0.001), and axitinib (p < 0.001) in 8505C and SW1736 cells. The combination of dabrafenib and axitinib inhibited cell invasion significantly more compared with vehicle (p < 0.0001 and p < 0.001) in both cell lines. (D) The histogram represents the mean number of cells that invaded the membrane/field of image. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. For all panels, the black stars denote combination versus vehicle, the blue stars denote combination versus BRAF inhibitor (PLX4720 and dabrafenib), and the red stars denote combination versus axitinib.