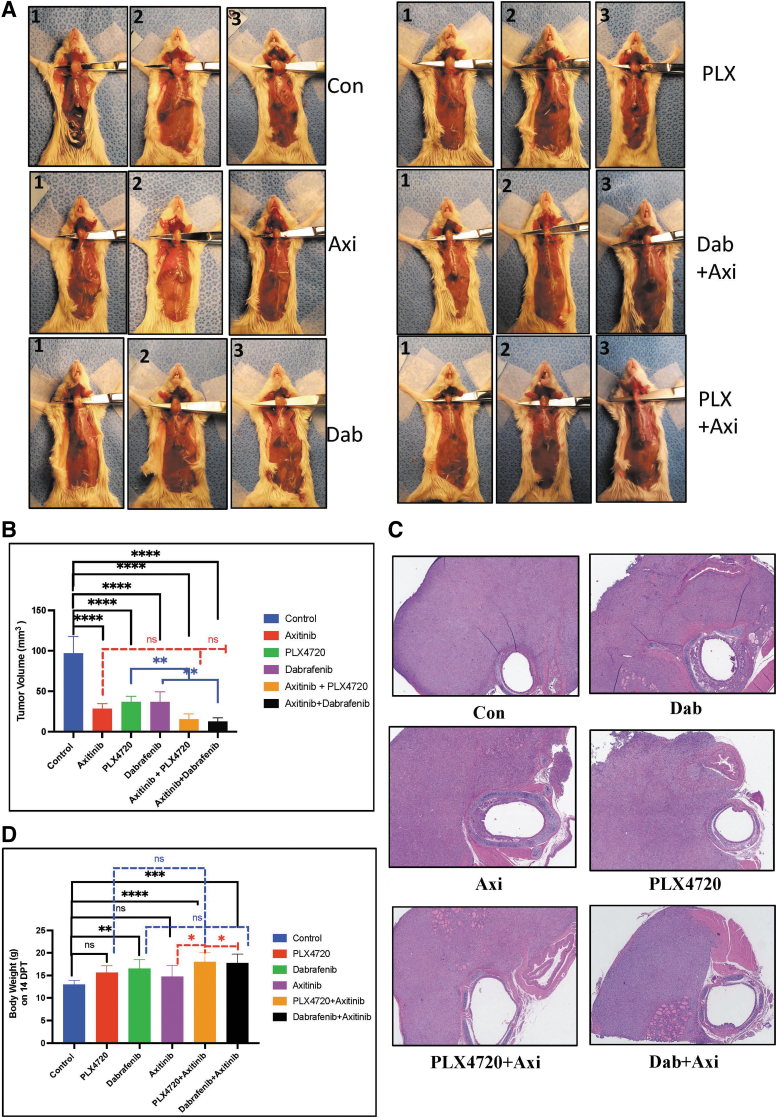
FIG. 5.
Effect of combination BRAF inhibition and axitinib treatment in vivo. (A, B) The combination of BRAF inhibitors and axitinib reduces tumor growth in vivo. The combination of PLX4720 and axitinib significantly reduced tumor growth compared with vehicle group (84%, p < 0.0001) and the PLX4720 group (p < 0.01). In the groups treated with each agent alone (PLX4720, 62%; axitinib, 70%), there was significant difference compared with the vehicle group (p < 0.0001). The combination of dabrafenib and axitinib significantly reduced tumor growth compared with the vehicle group (86%, p < 0.0001) and the dabrafenib group (p < 0.01). In the dabrafenib group (Dab, 61%), there was a significant difference compared with the vehicle group (p < 0.0001). (C) Pathological representative images of H and E staining of thyroid tumor from each group (original × 4 size). (D) The mice in the dabrafenib, PLX720+axitinib, and dabrafenib+axitinib groups weighed significantly more than the mice in the vehicle group (p < 0.0001) and the axitinib group (p < 0.01) on the last day of treatment (day 14). The mice in the vehicle, PLX4720, and axitinib groups had significantly lower body weights compared with the combination treatment group (29.4 ± 3.2 g; p < 0.05), who maintained their body weight and showed no signs of illness or cachexia. For all panels, the black stars denote vehicle versus other groups, the blue stars denote BRAF inhibitor (PLX4720 and dabrafenib) vs combination groups, and the red stars denote axitinib vs combination groups.