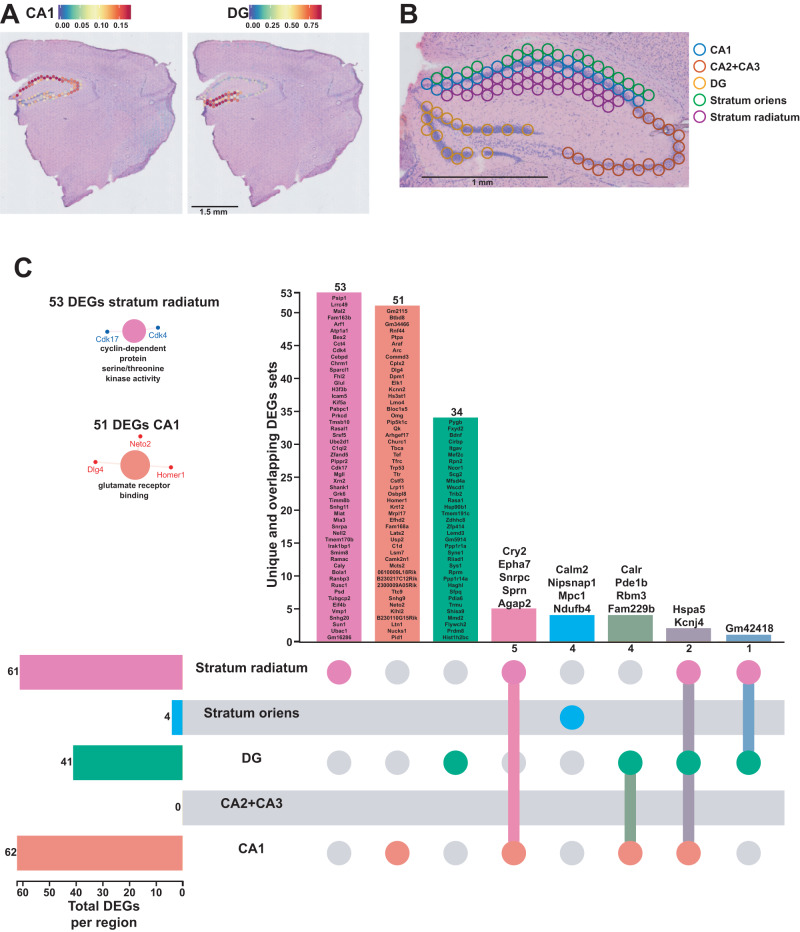
Fig. 3. Each hippocampal subregions displays a unique transcriptional impact of sleep deprivation.
A Prediction score of the deconvolution step for each of the 2085 spots of a representative example slice for CA1 pyramidal layer and dentate gyrus (DG) granule cells are represented with the color legend from blue to red. The rest of the subregions were selected based on biological knowledge using anatomical structures apparent on the H&E staining images. B Example of identified hippocampal subregions on sample 16. C UpSet plot of interactions between each hippocampal subregion. The number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) submitted for each subregion is represented by the histogram on the left (0–62 range). A gene is significant if its FDR step-up <0.1 and its log2fold-change ≥ |0.2 | . Dots alone indicate no overlap with any other lists. Dots with connecting lines indicate one or more overlap of DEGs between hippocampal subregion. The number of DEGs in a specific list of overlap is represented by the histogram on the top. Genes are labeled for the smallest lists. The unique lists of 53 DEGs and 51 DEGs for stratum radiatum and CA1 pyramidal cells respectively enriched specific molecular functions displayed on the left. The size of the circle for each enriched molecular function is proportional to the significance. Only molecular functions with a corrected p < 0.05 are displayed (two-sided hypergeometric test, Bonferroni step down). A gene is considered significant if FDR < 0.001 and log2fold change > |0.2 | .