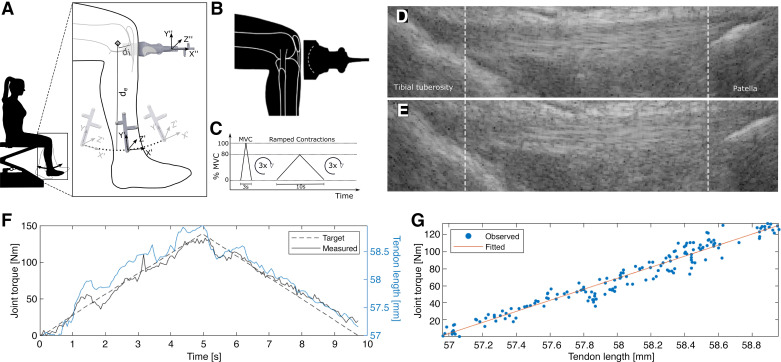
Figure 1.
Schematic of the measurement procedure used to determine the tensile properties of the patellar tendons. A: the subject performed knee flexion-extension, during which the shank trajectory was recorded with an optical tracking system to locate the instantaneous axis of knee rotation. Subsequently, an optically tracked ultrasound transducer was used to determine the extensor apparatus’s internal moment arm (di). de: external moment arm. B: patellar tendon elongation during isometric contraction was tracked with a convex ultrasound transducer. C: voluntary contraction profile used in the study. D: exemplary ultrasound tendon length measurement during voluntary contraction at low and high tendon stress (E). F: linear ramped contraction torque superimposed with the corresponding tendon length measurement. G: tendon length with respect to the produced joint torque was fitted with a linear regression to estimate tendon stiffness. MVC, maximum voluntary contraction.