FIGURE 5.
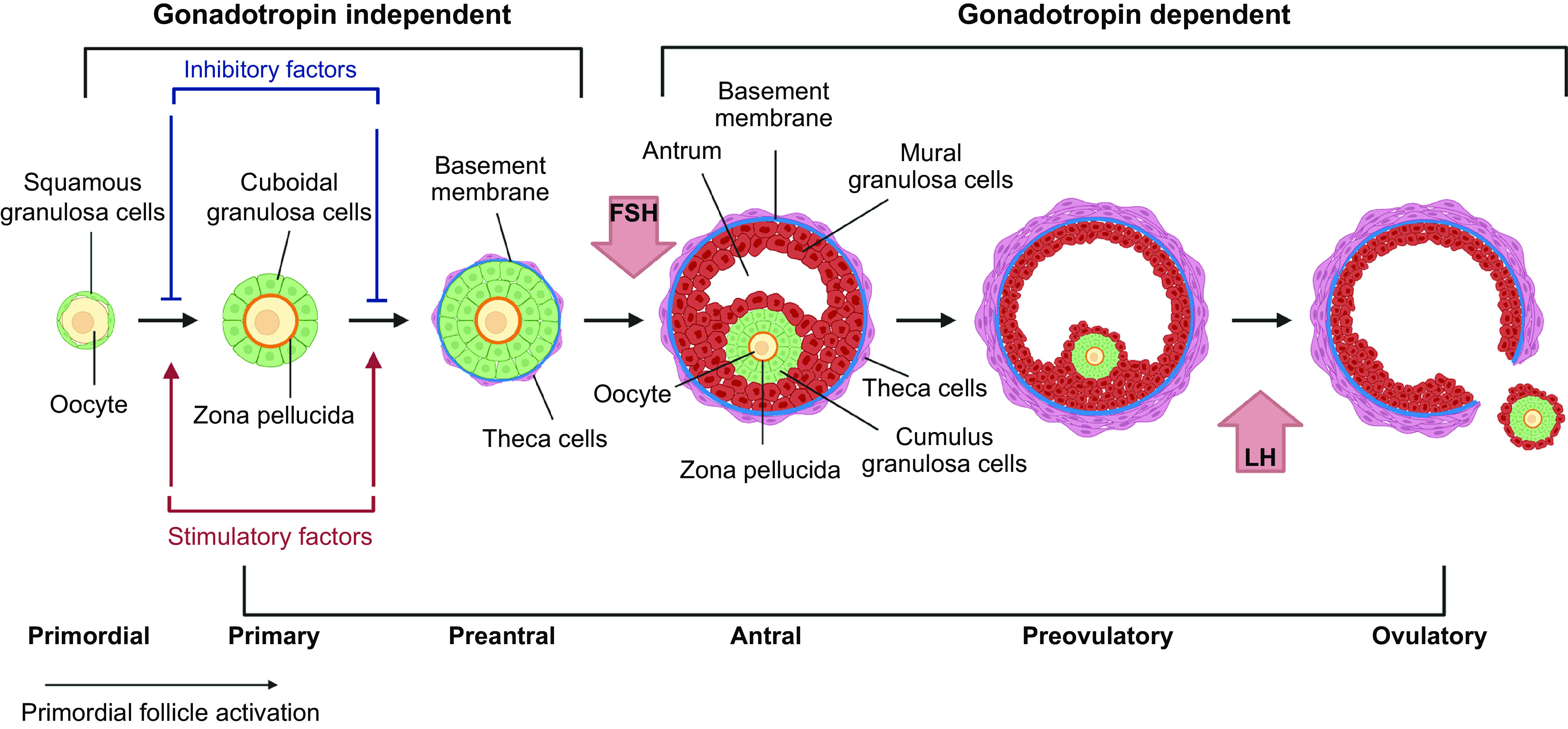
Stages of follicle growth (primordial to preovulatory). Primordial follicles are activated grow to the primary stage which is characterized by the oocyte being surrounded by a complete layer of cuboidal granulosa cells. Under the regulation of paracrine factors, granulosa cells proliferate to form multilaminar structures (preantral), which have differentiated thecal cells organized out with the basement membrane. Follicles then form a fluid filled cavity (antral) with mural granulosa cells lining the wall of the follicle and cumulus granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte. Antral follicles undergo rapid growth to reach preovulatory stages with the oocyte-cumulus complex being released at ovulation in response to luteinizing hormone (LH) signaling. Early stages grow independently of the gonadotropin follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), but multilaminar stages are acutely dependent on FSH for further growth. Image created with BioRender.com, with permission.
