-
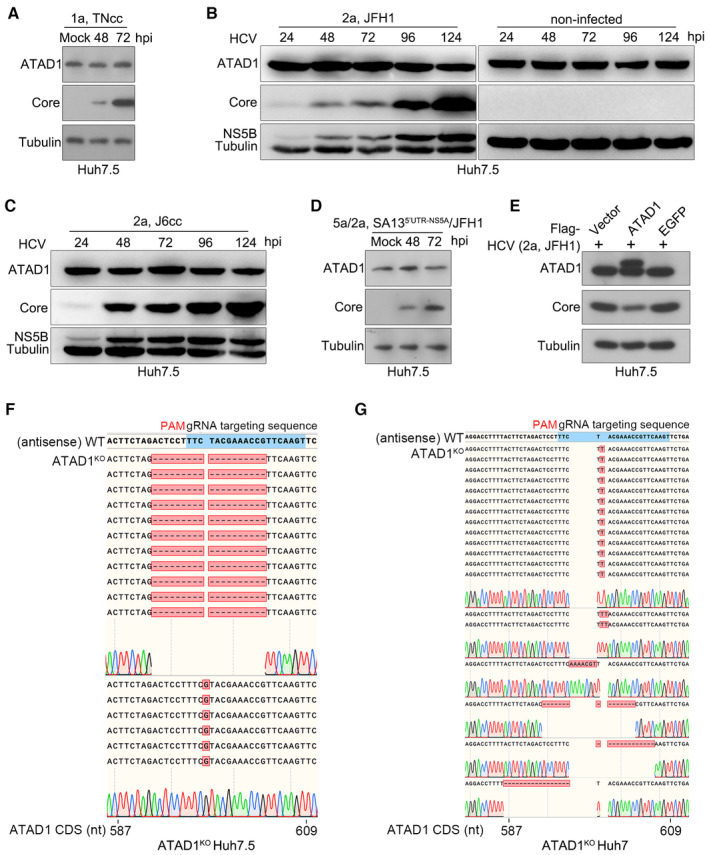
A
Huh7.5 cells were infected with HCV genotype 1a TNcc for 48 and 72 h, and total ATAD1 and HCV Core proteins were detected by western blotting.
-
B, C
Huh7.5 cells were infected with genotypes 2a clones, JFH1 (B) and J6cc (C), and the cells were harvested at 24, 48, 72, 96, and 124 h post‐infection (hpi). The expression levels of ATAD1, HCV Core, and NS5B were determined by western blotting. The cells without virus infection were treated in parallel as control.
-
D
Huh7.5 cells were infected with HCV intergenotypic recombinant (5a/2a; SA135′UTR‐NS5A/JFH1) for 48 and 72 h, then the expression levels of ATAD1 and Core were determined by western blotting.
-
E
Huh7.5 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag‐ATAD1, Flag‐EGFP, and Flag‐vector for 24 h, then the cells were infected with HCV 2a JFH1 for 48 h. The cells were harvested and analyzed by western blotting using anti‐Core and anti‐ATAD1 antibodies. In panels (A–E), tubulin was detected as an internal control.
-
F, G
Sequencing analysis of the genome of ATAD1KO Huh7.5 cells (F) and ATAD1KO Huh7 cells (G). The genomic DNAs of ATAD1KO Huh7.5 and Huh7 cells were extracted, and a region spanning sgATAD1‐RNA‐targeting sequence was amplified by PCR. The PCR products were cloned and subjected to Sanger sequencing analysis. For ATAD1KO Huh7.5 cells (F), 17 clones were sequenced, of which 1‐nt insertion (n = 6) and 19‐nt deletion (n = 11) were identified in the clonal analysis. For ATAD1KO Huh7 cells (G), 19 PCR product clones were sequenced, of which 1‐nt insertion (n = 13), 2‐nt insertion (n = 2), 7‐nt insertion (n = 1), 15‐nt deletion (n = 1), 13‐nt deletion (n = 1), and 17‐nt deletion (n = 1) were identified in the clonal analysis.