Fig 7. S. aureus and L. braziliensis co-infection increase the inflammatory responses in an IL-1 dependent manner.
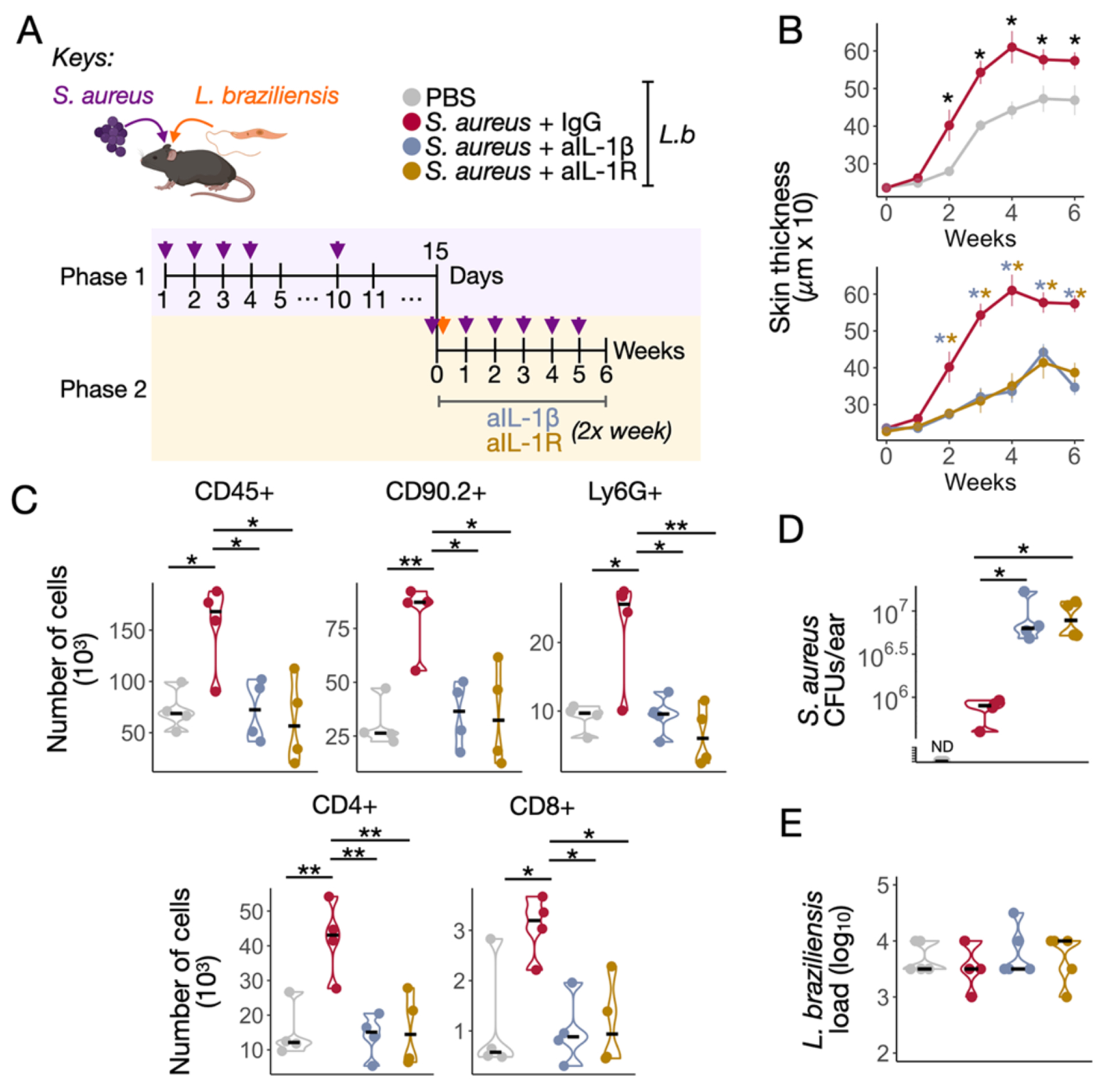
A) Schematic representation of S. aureus and L. braziliensis treatment protocol in C57BL/6 mice divided in Phase 1: pre-S. aureus colonization, and Phase 2: L. braziliensis infection course and blockade of IL-1β and IL-1R with monoclonal antibodies. Isotype IgG was used as a controlled treatment. The data shown are from one representative of two experiments (4–5 animals per group). B) Ear thickness measurements over time in mice. C) Number of CD45+, CD90.2+, Ly6G+, CD4+ and CD8+ cells recovered from the co-infected ears. D) Recovered pink S. aureus colony forming units (CFUs), and E) Parasite loads in the ear of different treatment groups in week six. Non-parametric Mann-Whitney test was used for statistical significance, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Violin plots and median are represented in the plots.
