Figure 4. Binary toxin regulator cdtR contributes to C. difficile virulence in mice.
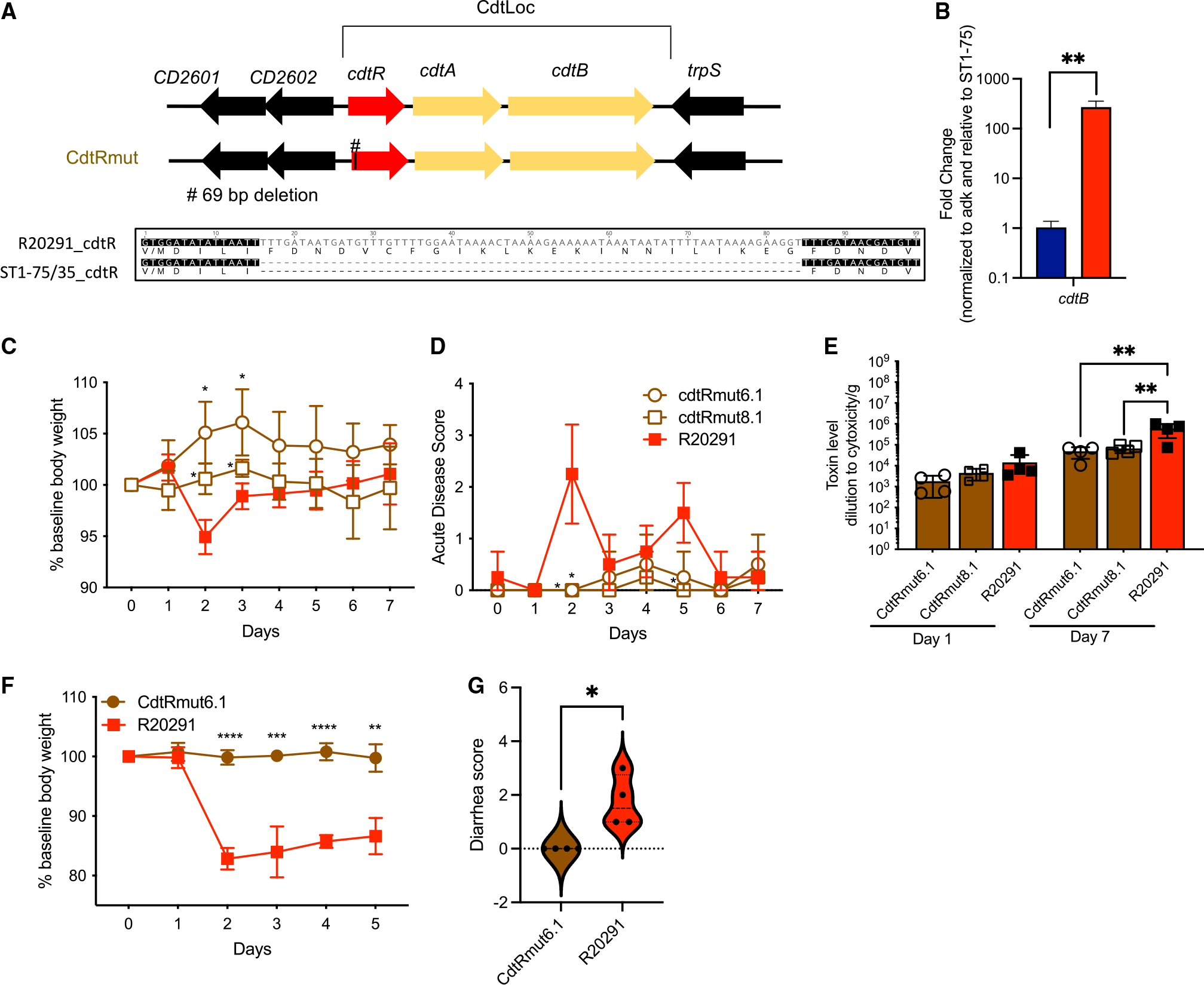
(A) Deletion identified in ST1-35/75 and schematic of cdtR mutants generated using R20291 C. difficile strain.
(B) Germ-free mice (n = 3 per group) orally administered with 200 spores of indicated C. difficile strains. Binary toxin gene cdtB transcripts were measured by RT-qPCR on cecal contents harvested at 24 h post-infection with 2 technical replicates per sample. Transcripts were normalized to the adk, and fold change is relative to ST1-75 condition.
(C–E) Wild-type C57BL/6 mice (n = 3 to 5 per group) were treated with MNV and clindamycin as previously described. Then, mice were inoculated with 200 C. difficile spores via oral gavage. Daily body weight and acute disease scores were monitored for 7 days post-infection.
(C) Percentage of weight loss to baseline of mice infected with indicated strains. Both CdtRmut6.1 and CdtRmut8.1 have significant differences on days 2 and 3 compared with R20291.
(D) Acute disease scores comprising weight loss, body temperature drop, diarrhea, and morbidity of mice infected with indicated strains. CdtRmut6.1 has a significant difference on day 2 compared with R20291. CdtRmut8.1 has a significant difference on days 2 and 5 compared with R20291.
(E) Fecal Tcd toxins measured by CHO cell rounding assay on indicated days.
(F and G) Germ-free mice (n = 4) orally administered with 200 spores of indicated C. difficile strains. Daily body weight and were monitored for 5 days post-infection.
(F) Percentage of weight loss to baseline of mice infected with indicated strains.
(G) Diarrhea scores of mice infected with indicated strains 3 days post-infection (violin plot showing all points). Results represent means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
