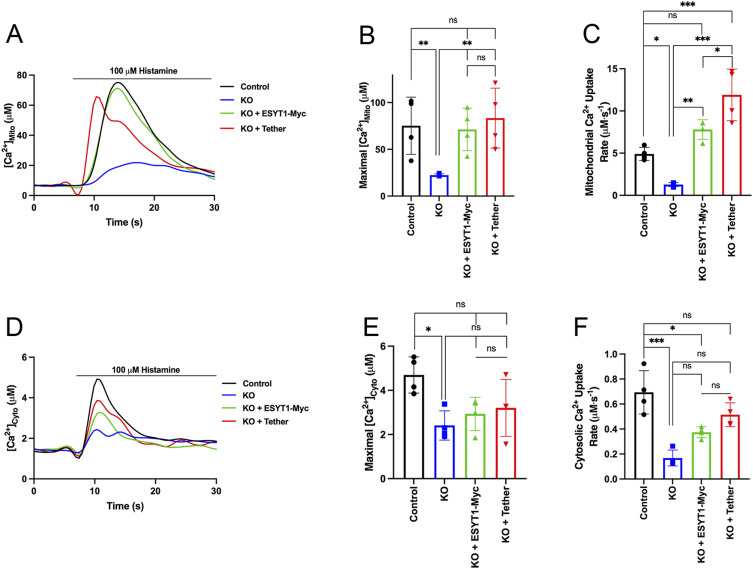
Figure S3. ESYT1 is required for ER to mitochondria Ca2+ transfer.
(A) Trace of mitochondrial–aequorin measurements of mitochondrial Ca2+ upon histamine stimulation (100 μM) in control human fibroblasts, ESYT1 knock-out fibroblasts, ESYT1 knock-out fibroblasts expressing either ESYT1–Myc or an artificial mitochondria–ER tether. (B) Quantification of maximal mitochondrial Ca2+. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. From >50 cells per condition; n = 4 independent experiments. ns: not significant; **P < 0.01 (Turkey’s multiple comparisons test). (C) Quantification of the rate of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. From >50 cells per condition; n = 4 independent experiments. ns: not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (Turkey’s multiple comparisons test). (D) Trace of cytosolic–aequorin measurements of cytosolic Ca2+ upon histamine stimulation (100 μM) in control human fibroblasts, ESYT1 knock-out fibroblasts, ESYT1 knock-out fibroblasts expressing either ESYT1–Myc or an mitochondria–ER artificial tether. (E) Quantification of maximal cytosolic Ca2+. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. From >50 cells per condition; n = 4 independent experiments. ns: not significant; *P < 0.05 (Turkey’s multiple comparisons test). (F) Quantification of the rate of cytosolic Ca2+ uptake. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. From >50 cells per condition; n = 4 independent experiments. ns: not significant; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 (Turkey’s multiple comparisons test).