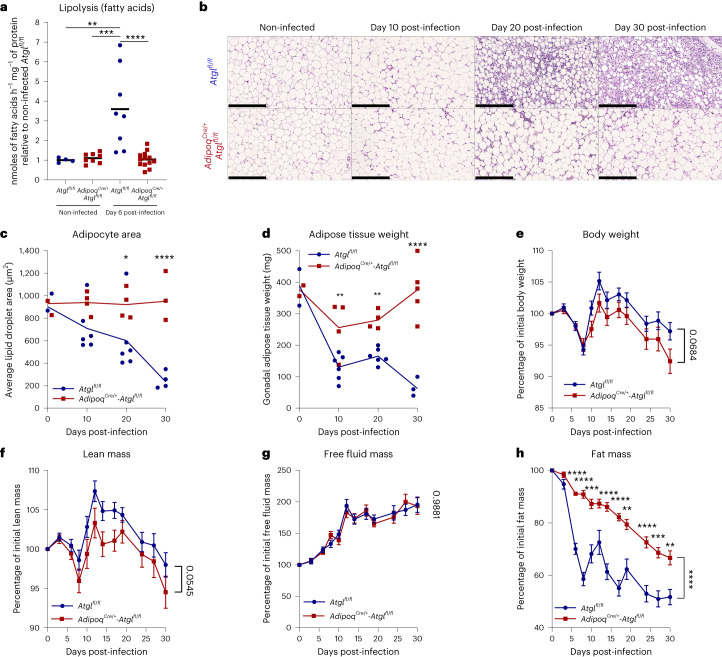
Fig. 3. ATGL deficiency in adipocytes prevents T. brucei-induced lipolysis and reduces global loss of fat mass.
a, Release of FFAs from gonadal AT explants of infected and non-infected Atglfl/fl (WT) and AdipoqCre/+-Atglfl/fl (KO) mice. n = 4 non-infected and 8 infected Atglfl/fl mice and 8 non-infected and 13 infected AdipoqCre/+-Atglfl/fl mice examined over two independent experiments. b, Representative gonadal AT haematoxylin and eosin micrographs (20× magnification; scale bar, 250 µm). c, Lipid droplet area of adipocytes in tissue sections of the gonadal AT. d, Total weight of the gonadal AT at different timepoints post-infection. For days 0, 10, 20 and 30, n = 3, 6, 6 and 5 Atglfl/fl mice and 3, 4, 4 and 5 AdipoqCre/+-Atglfl/fl mice were examined, respectively, in a single experiment (c and d). e–h, Total body weight (e), lean mass (f), free fluid mass (g) and fat mass (h) relative to baseline. n = 32 Atglfl/fl and 27 AdipoqCre/+-Atglfl/fl mice examined over four independent experiments (e–h). Error bars represent the s.e.m. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA (a) or two-way ANOVA (c and d) or mixed-effects two-way ANOVA (e–h) using Šidák’s test for multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Statistical source data contain additional parameters.