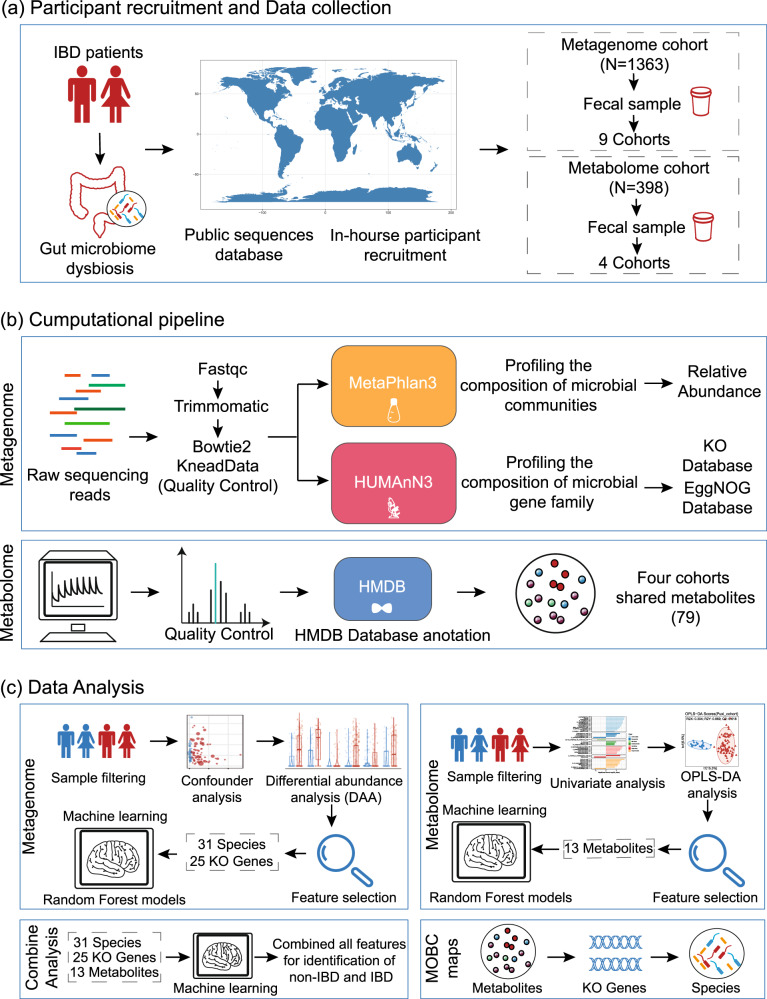
Fig. 1. Workflow for cross-cohort integration analysis of fecal metagenomics and metabolomics in IBD.
a We included a total of 9 fecal metagenomic cohorts (n = 1363) and 4 metabolomic cohorts (n = 398) from diverse geographic locations worldwide. b We utilized the MetaPhlan3 tool for taxonomic profiling and HUMAnN3 for functional profiling to reprocess all raw metagenomic sequencing data. Additionally, we annotated the compound names from the metabolomics analysis with the same ID number using the HMDB (Human Metabolome Database). c Through strict sample filtering, detailed bioinformatics analysis, and feature selection, we identified a series of representative features, including 31 bacterial features, 25 KO genes, and 13 metabolites. Subsequently, we developed machine learning models and used the features for the diagnosis of IBD. Finally, we introduced the multi-omics biological correlation (MOBC) maps framework to shed light on the interconnected relationships among gut bacteria, metabolites, and KO genes in IBD.