Figure 2.
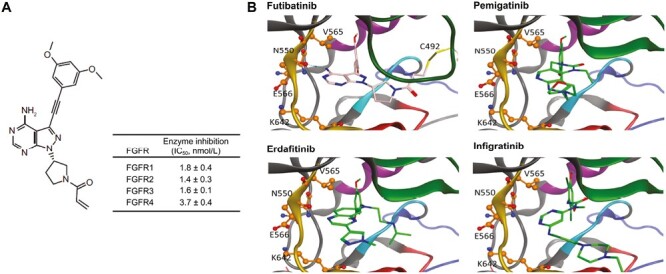
Futibatinib structure and predicted binding of futibatinib and other reversible FGFR inhibitors to the FGFR kinase domain. (A) Chemical structure of futibatinib and in vitro inhibitory activity. Adapted from Cancer Research, 2020, 80(22), 4986-4997, Sootome H, Fujita H, Ito K, et al., Futibatinib Is a Novel Irreversible FGFR 1-4 Inhibitor That Shows Selective Antitumor Activity against FGFR-Deregulated Tumors, with permission from AACR.11(B) Predicted interactions of futibatinib, erdafitinib, and pemigatinib with the ATP binding pocket of the FGFR2 wild-type kinase domain. Amino acid residues altered in identified resistance mutations are labeled and shown as ball and stick models. Kinase domain regions are depicted as follows: gold, hinge region; red, catalytic loop; blue, activation domain; purple, c-alpha-helix; green, P-loop; cyan, DFG motif. Futibatinib (pink and blue stick figure) binds covalently to C492 in the P-loop (yellow stick), enabling it to persist in the ATP-binding pocket irrespective of the presence of resistance mutations, which block access of reversible FGFR inhibitors such as erdafitinib, pemigatinib, or infigratinib (green and blue stick figures). Reproduced with permission from Goyal et al. 2023.48 Abbreviations: DFG, Asp-Phe-Gly; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptors; IC50, half-maximal inhibitory concentration. From The New England Journal of Medicine, Goyal L, Meric-Bernstam F, Hollebecque A, et al., Futibatinib for FGFR2-Rearranged Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, 388, 228-239. Copyright © (2023) Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.
