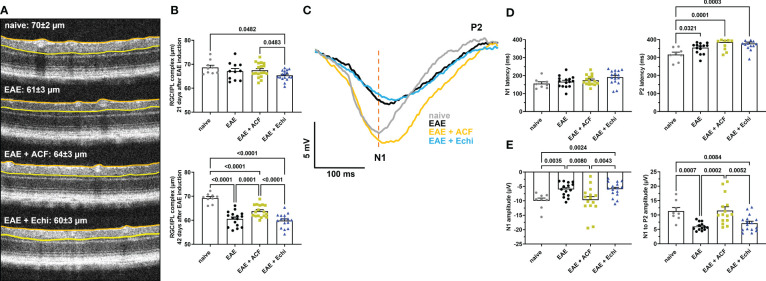
Figure 2.
ACF treatment ameliorated degeneration of RGC structure and optic nerve function. (A) Representative OCT images demonstrate thinning of the RGC/ILP complex, outlined by the orange and yellow line, in treated and untreated EAE mice 42 days after immunization. (B) Measurements of the RGC/IPL complex over time revealed progressive decrease in thickness in all EAE groups, whereas ACF treatment significantly improved the outcome of RGC/IPL complex thinning. (C) Group-averaged pattern VEP trace overlays displayed significant changes in amplitudes, N1 latency, and P2 conduction speed. (D) Analysis of pattern VEP recordings revealed a significant delay of the P2 latency. (E) Similar to the RGC/IPL complex thinning, declines in the pattern VEP amplitudes were observed in the EAE and EAE+Echi groups. In contrast, ACF treatment facilitated preservation of the N1 and N1-to-P2 amplitudes in EAE mice. Points on graphs represent measurements of individual eyes. All data are given as mean ± SEM, and individual data points show the average value of both eyes per sample. Differences between groups were calculated using a mixed-effect model with Tukey post hoc test.