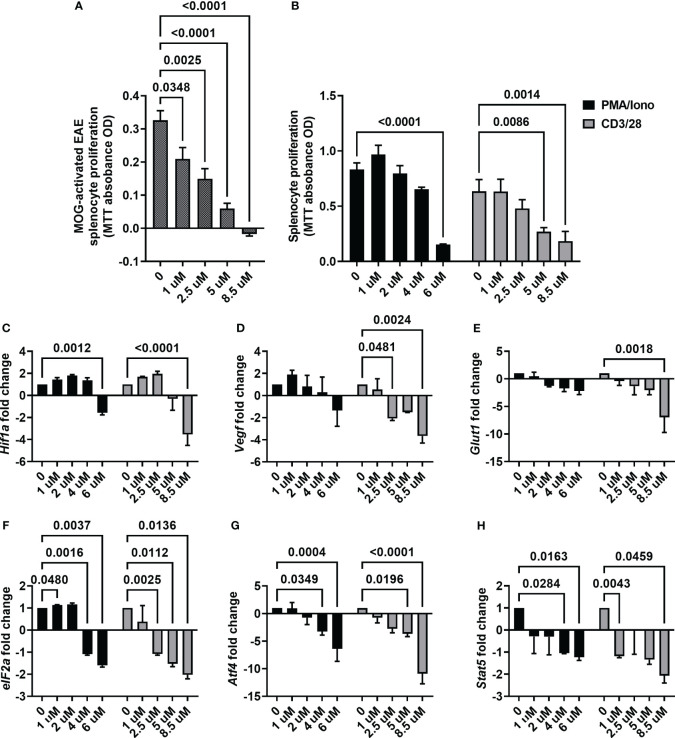
Figure 5.
ACF immunomodulatory properties on activated splenocytes. (A) ACF demonstrated a dose-dependent decrease in the proliferation of splenocytes from EAE mice that were restimulated with MOG33-55 (shaded gray bars) and similar immunomodulatory effects on PMA/Iono (black bars)- or CD3/28 beads (gray bars)-stimulated naïve splenocytes (B). Examination of changes in HIF-1 pathway-relevant genes revealed target engagement in stimulated naïve splenocytes with a dose-dependent downregulation of Hif1-a (C), Vegf (D), and Glut1 (E) expression. Furthermore, ACF facilitated blocking of UPR, evident by the downregulation of eIF2a (F) and Atf4 (G) expression, and negatively affected Stat5 expression in a dose-dependent manner (H).