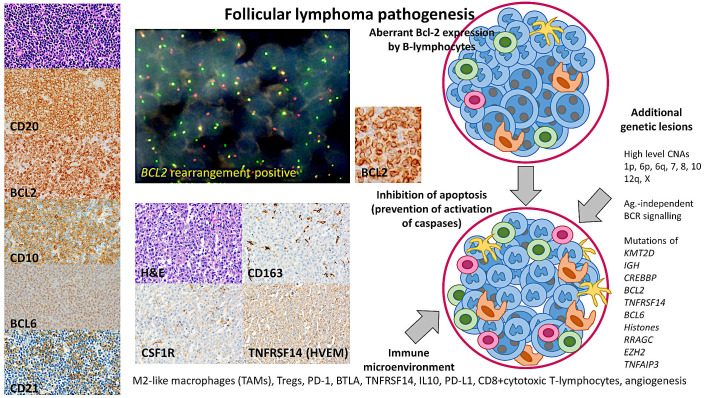
Fig. 3.
Pathogenesis of follicular lymphoma
The pathogenesis of follicular lymphoma is multifactorial; and involves a series of steps in which a B lymphocyte acquires genetic and epigenetic alterations that lead to the malignant transformation. The pathobiology includes genetic alterations in BCL2 and BCL6, a mutational profile, and changes in the immune microenvironment and the immune checkpoint. On the left, a characteristic low-grade follicular lymphoma is shown. This case was characterized by a nodular proliferation of centrocytes, which had a classical phenotype with positivity of CD20, CD10, BCL6, and BCL2, and a mesh of CD21 follicular dendritic cells. CNAs, copy number alterations.