Figure 4.
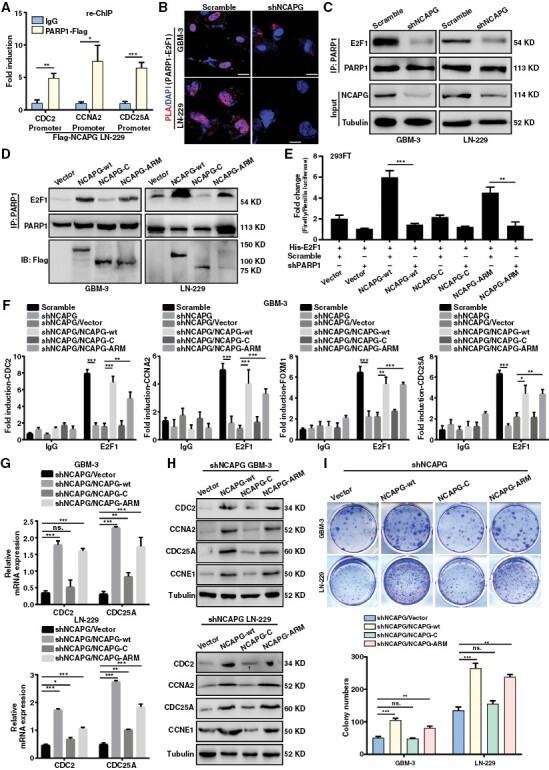
Nonstructural maintenance of chromatin condensin I complex subunit G (NCAPG) promotes glioblastoma (GBM) progression via Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1)-mediated E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1) transactivation. (A) ChIP-re-ChIP assay indicating the E2F1 target promoters were co-regulated by NCAPG and PARP1 in LN-229/Flag-NCAPG cells. (B) Duo-link PLA assay was performed to detect the effect of NCAPG knockdown on the interaction between PARP1 and E2F1 in GBM cells. (C) Co-IP assay was used to determine the binding affinity of PARP1 and E2F1 protein caused by NCAPG knockdown. (D) Co-IP assay was used to determine the function of NCAPG domain for facilitating the interaction of PARP1 and E2F1. (E) The Dual-Luciferase reporting gene assay was used to determine the function of NCAPG domain on E2F1 activity. (F) ChIP assays were performed to detect the function of NCAPG domain on the enrichment of E2F1 to its target promoters. (G, H) The mRNA and protein expression of E2F1 downstream targets were examined in GBM cells to detect the function of NCAPG domain on E2F1 target genes. (I) Colony formation assay was used to detect the function of NCAPG domain on cell proliferation of GBM cells. All data are shown as the means ± SD; *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.
